Vaccinations Around The World
Introduction to Vaccinations
Vaccinations have been a crucial part of public health for decades, playing a significant role in preventing the spread of infectious diseases. Vaccines work by introducing a small, harmless piece of a pathogen, such as a virus or bacteria, to the body, which then triggers the immune system to produce antibodies and immune cells that can recognize and attack the pathogen. This helps to build immunity against future infections, protecting not only the individual but also the community as a whole. With the advancement of medical science, various types of vaccines have been developed, including inactivated vaccines, live attenuated vaccines, conjugate vaccines, recombinant vaccines, and mRNA vaccines.
History of Vaccinations
The concept of vaccination dates back to ancient times, with evidence of smallpox inoculation practices in China, India, and Africa as early as the 10th century. However, the modern era of vaccination began with the development of the smallpox vaccine by Edward Jenner in 1796. Since then, numerous vaccines have been developed, including vaccines for diseases such as rabies, diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, measles, mumps, rubella, polio, hepatitis B, haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib), and human papillomavirus (HPV). The introduction of these vaccines has led to a significant reduction in the incidence of infectious diseases worldwide.
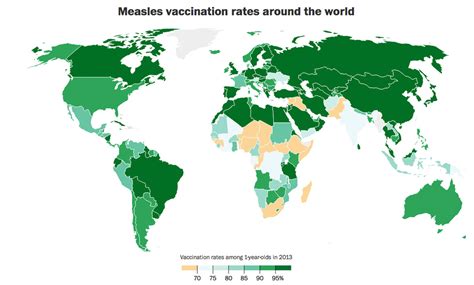
Vaccination Programs Around the World
Vaccination programs vary from country to country, depending on factors such as the local disease burden, healthcare infrastructure, and economic resources. In developed countries, vaccination programs are often well-established and widely accessible, with a strong focus on childhood vaccinations. In contrast, developing countries face numerous challenges, including limited access to vaccines, inadequate healthcare infrastructure, and lack of awareness about the importance of vaccinations. Despite these challenges, many developing countries have made significant progress in recent years, with the support of global health organizations such as the World Health Organization (WHO) and UNICEF.
Types of Vaccines
There are several types of vaccines, each with its own unique characteristics and advantages. Some of the most common types of vaccines include: * Inactivated vaccines: These vaccines contain killed or inactivated pathogens, which cannot cause the disease but still stimulate an immune response. * Live attenuated vaccines: These vaccines contain weakened or attenuated pathogens, which can cause a mild infection but still provide immunity. * Conjugate vaccines: These vaccines combine a weakened pathogen with a carrier protein to enhance immune response. * Recombinant vaccines: These vaccines use genetic engineering to produce specific proteins or antigens. * mRNA vaccines: These vaccines use a piece of genetic material called messenger RNA (mRNA) to instruct cells to produce a specific protein or antigen.
Vaccine Development and Approval
The development and approval of vaccines involve a rigorous process, including: * Research and development: Scientists identify a potential vaccine candidate and conduct initial studies to assess its safety and efficacy. * Preclinical trials: The vaccine is tested in laboratory and animal studies to assess its safety and immunogenicity. * Clinical trials: The vaccine is tested in human subjects to assess its safety and efficacy. * Regulatory approval: The vaccine is reviewed and approved by regulatory agencies, such as the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). * Post-marketing surveillance: The vaccine is monitored for safety and efficacy after it is released to the market.
Challenges and Controversies
Despite the many benefits of vaccinations, there are also challenges and controversies surrounding their use. Some of the key issues include: * Vaccine hesitancy: Some individuals may be hesitant to receive vaccines due to concerns about safety, efficacy, or potential side effects. * Vaccine misinformation: The spread of misinformation about vaccines can lead to confusion and mistrust among the public. * Vaccine shortages: Shortages of vaccines can occur due to manufacturing issues, supply chain disruptions, or increased demand. * Vaccine equity: There may be disparities in access to vaccines, particularly in developing countries or among marginalized populations.
Future Directions
The future of vaccinations looks promising, with ongoing research and development of new vaccines and technologies. Some of the key areas of focus include: * Emerging diseases: The development of vaccines for emerging diseases, such as COVID-19, Ebola, and Zika. * Cancer vaccines: The development of vaccines that can prevent or treat cancer. * Gene editing: The use of gene editing technologies, such as CRISPR, to develop new vaccines. * Vaccine delivery: The development of new vaccine delivery systems, such as microneedles and nanoparticles.
💡 Note: It's essential to stay informed about the latest developments in vaccine research and development to address the ongoing challenges and controversies surrounding vaccinations.
In summary, vaccinations have been a crucial part of public health for decades, and their importance cannot be overstated. By understanding the history, types, and challenges surrounding vaccinations, we can work towards a future where everyone has access to these life-saving interventions. The ongoing research and development of new vaccines and technologies will continue to shape the landscape of public health, and it’s essential to stay informed and engaged in the conversation.
What is the difference between inactivated and live attenuated vaccines?
+
Inactivated vaccines contain killed or inactivated pathogens, while live attenuated vaccines contain weakened or attenuated pathogens. Inactivated vaccines are generally safer but may require booster shots, while live attenuated vaccines can provide longer-lasting immunity but may carry a small risk of infection.
How are vaccines developed and approved?
+
Vaccines are developed through a rigorous process, including research and development, preclinical trials, clinical trials, regulatory approval, and post-marketing surveillance. The development and approval of vaccines involve multiple stakeholders, including scientists, regulatory agencies, and healthcare professionals.
What are some of the challenges and controversies surrounding vaccinations?
+
Some of the key challenges and controversies surrounding vaccinations include vaccine hesitancy, vaccine misinformation, vaccine shortages, and vaccine equity. These issues can be addressed through education, awareness, and access to accurate information, as well as ongoing research and development of new vaccines and technologies.