CDC Immunization Guidelines
Introduction to CDC Immunization Guidelines
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) plays a crucial role in protecting public health and safety in the United States. One of the key strategies for achieving this goal is through the development and implementation of immunization guidelines. Immunization is the process whereby a person is made immune or resistant to an infectious disease, typically by the administration of a vaccine. The CDC’s immunization guidelines are designed to provide healthcare professionals, parents, and patients with the latest information on recommended vaccines, vaccination schedules, and contraindications to vaccination.
Understanding the Importance of Immunization
Immunization is widely recognized as one of the most effective ways to prevent infectious diseases and protect public health. By following the CDC’s immunization guidelines, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of contracting serious and potentially life-threatening diseases, such as measles, mumps, rubella, polio, and influenza. Moreover, immunization not only protects the individual who receives the vaccine but also helps to prevent the spread of disease in the community, thereby protecting vulnerable populations, such as the elderly, young children, and people with weakened immune systems.
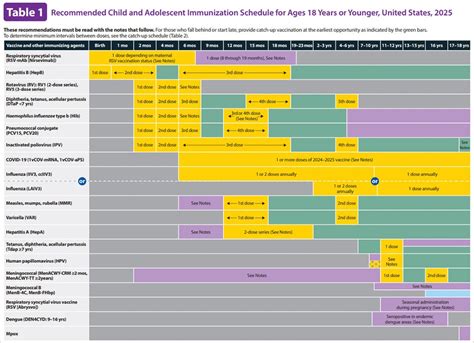
CDC Recommended Immunization Schedule
The CDC recommends a series of vaccines for individuals of all ages, from infancy to adulthood. The recommended immunization schedule is designed to provide protection against a range of infectious diseases, including:
- DTaP (diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis)
- Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib)
- HPV (human papillomavirus)
- MMR (measles, mumps, and rubella)
- PCV (pneumococcal conjugate)
- Polio
- Rotavirus
Vaccine Safety and Contraindications
While vaccines are highly effective in preventing infectious diseases, they can also cause side effects and, in rare cases, serious adverse reactions. The CDC closely monitors vaccine safety and provides guidance on contraindications to vaccination, such as:
- Severe allergic reactions to vaccine components
- Weakened immune systems, such as HIV/AIDS or cancer
- Pregnancy or breastfeeding, for certain vaccines
Special Considerations for Vaccination
Certain individuals may require special consideration when it comes to vaccination, including:
- Pregnant women, who may need to avoid certain vaccines or take special precautions
- Travelers, who may need additional vaccines or medications to protect against diseases prevalent in their destination
- People with weakened immune systems, who may require additional vaccines or special precautions to prevent disease
💡 Note: It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before receiving any vaccine, especially if you have any underlying medical conditions or concerns.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
In summary, the CDC’s immunization guidelines play a vital role in protecting public health and preventing infectious diseases. By following the recommended immunization schedule, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of contracting serious diseases and help to prevent the spread of disease in the community. It is essential to stay informed about the latest developments in vaccine science and to consult with a healthcare professional before receiving any vaccine. By working together, we can promote a healthier and safer community for everyone.
What is the purpose of the CDC’s immunization guidelines?
+
The CDC’s immunization guidelines aim to provide healthcare professionals, parents, and patients with the latest information on recommended vaccines, vaccination schedules, and contraindications to vaccination, to promote public health and prevent infectious diseases.
What vaccines are recommended for infants and young children?
+
The CDC recommends a series of vaccines for infants and young children, including DTaP, Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib), HPV, MMR, PCV, polio, and rotavirus, to provide protection against a range of infectious diseases.
Can vaccines cause side effects or serious adverse reactions?
+
While vaccines are highly effective in preventing infectious diseases, they can also cause side effects and, in rare cases, serious adverse reactions. The CDC closely monitors vaccine safety and provides guidance on contraindications to vaccination.