CDC Recommendations Guide
Introduction to CDC Recommendations
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) provides crucial guidance on various health topics, including disease prevention, vaccination, and infection control. These recommendations are based on extensive research and are designed to protect public health. Understanding and following CDC recommendations is essential for individuals, healthcare providers, and communities to maintain and improve health outcomes. In this guide, we will delve into the key areas where CDC recommendations play a vital role, such as vaccine schedules, travel health, and infectious disease management.
Vaccine Schedules and Recommendations
Vaccination is one of the most effective ways to prevent infectious diseases. The CDC issues schedules and recommendations for vaccines to ensure that individuals of all ages are protected against vaccine-preventable diseases. These schedules are regularly updated to reflect new vaccine approvals, changes in disease epidemiology, and the latest scientific evidence. Key areas include: - Childhood Vaccines: Vaccines recommended for children from birth through adolescence, including hepatitis B, rotavirus, DTaP, Hib, PCV, IPV, MMR, varicella, and HPV vaccines. - Adult Vaccines: Recommendations for adults, such as Tdap, MMR, varicella, HPV, pneumococcal, and influenza vaccines, to protect against diseases that can affect adults. - Travel Vaccines: Guidance on vaccines needed for international travel, depending on the destination, to prevent diseases such as yellow fever, typhoid, and hepatitis A.
Travel Health and Vaccinations
Before traveling abroad, it’s crucial to consult CDC travel health recommendations. These recommendations help travelers understand the health risks associated with their destinations and provide guidance on necessary vaccinations, medications, and preventive measures. The CDC categorizes travel health recommendations based on the level of risk: - Level 1 (Practice Usual Precautions): Destinations with low risk where usual precautions are recommended. - Level 2 (Practice Enhanced Precautions): Areas with moderate risk where enhanced precautions are advised. - Level 3 (Practice Enhanced Precautions or Avoid Nonessential Travel): High-risk areas where either enhanced precautions or avoidance of nonessential travel is recommended. - Level 4 (Do Not Travel): Very high-risk areas where travel should be avoided due to serious risks to safety and security.
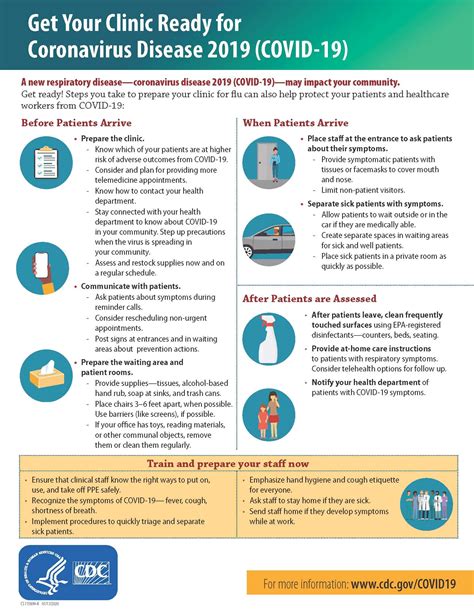
Infectious Disease Management
The CDC provides comprehensive guidance on managing infectious diseases, including prevention strategies, diagnostic approaches, treatment options, and infection control measures. For diseases like COVID-19, influenza, and tuberculosis, understanding CDC recommendations is vital for healthcare providers and the public. Key aspects include: - Prevention: Measures to prevent the spread of infectious diseases, such as hand hygiene, use of personal protective equipment (PPE), and social distancing. - Diagnosis: Guidance on diagnostic tests and interpretation to ensure accurate identification of infectious diseases. - Treatment: Recommendations for treatment, including antimicrobial therapy and supportive care, based on the latest evidence and guidelines.
Food Safety Recommendations
Food safety is another critical area where CDC recommendations play a significant role. The CDC provides guidance on safe food handling practices to prevent foodborne illnesses. Key recommendations include: - Cleaning: Regular cleaning of hands, utensils, and surfaces that come into contact with food. - Separation: Preventing cross-contamination by separating raw, cooked, and ready-to-eat foods. - Cooking: Cooking foods to the recommended internal temperature to ensure that harmful bacteria are killed. - Chilling: Keeping perishable foods at a safe temperature to prevent bacterial growth.
| Food Safety Practice | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Cleaning | Wash hands with soap and water for at least 20 seconds. |
| Separation | Use separate cutting boards and plates for raw meat, poultry, and seafood. |
| Cooking | Cook ground meats to an internal temperature of at least 160°F (71°C). |
| Chilling | Refrigerate perishable foods promptly and keep the refrigerator at 40°F (4°C) or below. |
📝 Note: Always consult the CDC website for the most current recommendations, as guidelines can change based on new evidence and emerging health issues.
Mental Health and CDC Recommendations
Mental health is an essential aspect of overall well-being. The CDC recognizes the importance of mental health and provides recommendations to support mental health, including stress management, coping with traumatic events, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Key recommendations include: - Stress Management: Techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, and exercise to manage stress. - Social Support: Building and maintaining strong social connections to support mental health. - Healthy Lifestyle: Engaging in regular physical activity, eating a balanced diet, and getting sufficient sleep to support mental well-being.
In summary, CDC recommendations cover a wide range of health topics, from vaccination and infectious disease management to food safety and mental health. Following these guidelines can significantly reduce the risk of diseases and promote overall health and well-being. It is essential for individuals, communities, and healthcare providers to stay informed about the latest CDC recommendations to make informed decisions about health.
What are the most current CDC recommendations for COVID-19 vaccination?
+
The CDC regularly updates its recommendations for COVID-19 vaccination. For the most current information, visit the CDC’s COVID-19 webpage, which includes guidance on vaccine eligibility, booster shots, and vaccine safety.
How do I find CDC travel health recommendations for my destination?
+
To find travel health recommendations for your destination, visit the CDC’s Travel Health website. You can search by country or disease to find information on recommended vaccines, medications, and precautions.
What are some key food safety recommendations to prevent foodborne illnesses?
+
Key food safety recommendations include cleaning hands and surfaces frequently, separating raw and cooked foods, cooking foods to the recommended internal temperature, and chilling perishable foods promptly. Following these practices can significantly reduce the risk of foodborne illnesses.