5 CDC Tips Africa
Introduction to CDC Tips for Africa
When traveling to Africa, it’s essential to prioritize health and safety. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) provides valuable tips and guidelines for travelers to ensure a safe and enjoyable trip. In this article, we will explore five crucial CDC tips for traveling to Africa, covering topics such as vaccinations, malaria prevention, and food safety.
Tip 1: Get the Necessary Vaccinations
Before traveling to Africa, it’s crucial to get the necessary vaccinations to protect against diseases such as yellow fever, hepatitis A, and typhoid. The CDC recommends that travelers consult their doctor or a travel clinic at least 4-6 weeks before their trip to determine the required vaccinations. Some vaccinations, such as the yellow fever vaccine, may be required for entry into certain African countries. It’s essential to note that some vaccinations may have side effects, so it’s crucial to discuss any concerns with a healthcare professional.
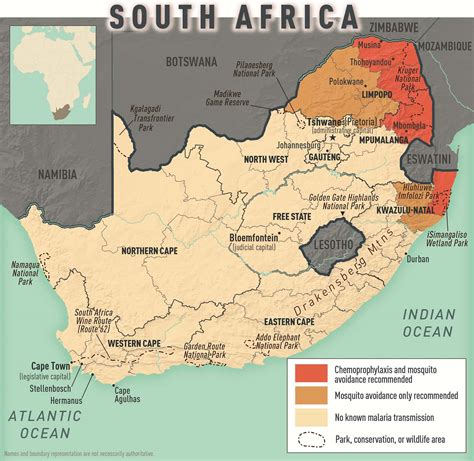
Tip 2: Prevent Malaria
Malaria is a significant health risk in many African countries, and the CDC recommends that travelers take precautions to prevent it. This includes taking antimalarial medication, using insecticide-treated bed nets, and wearing protective clothing. It’s also essential to apply insect repellent regularly, especially during peak mosquito hours. The CDC provides a list of recommended antimalarial medications and dosages on their website.
Tip 3: Practice Food and Water Safety
Food and water safety are critical when traveling to Africa. The CDC recommends that travelers drink bottled or filtered water, avoid eating undercooked meat or raw vegetables, and avoid consuming unpasteurized dairy products. It’s also essential to wash hands regularly, especially before eating. When eating at restaurants or street food stalls, make sure to choose establishments that appear clean and well-maintained.
Tip 4: Protect Against Insect-Borne Illnesses
In addition to malaria, other insect-borne illnesses such as dengue fever, chikungunya, and Zika virus are present in Africa. The CDC recommends that travelers take precautions to prevent these illnesses, including wearing protective clothing, applying insect repellent, and staying in air-conditioned or screened rooms. It’s also essential to eliminate standing water around living areas to prevent mosquito breeding.
Tip 5: Stay Safe in Crowded Areas
Crowded areas such as markets, bus stations, and airports can be breeding grounds for illnesses such as tuberculosis and meningitis. The CDC recommends that travelers take precautions to stay safe in these areas, including wearing a mask, avoiding close contact with people who are sick, and washing hands regularly. It’s also essential to be aware of pickpocketing and petty theft in crowded areas.
🌟 Note: It's essential to stay informed about local health concerns and outbreaks before and during your trip to Africa. The CDC provides up-to-date information on their website, and travelers can also register with their government's travel advisory program to receive important safety and security updates.
In summary, the CDC provides valuable tips and guidelines for travelers to Africa, covering topics such as vaccinations, malaria prevention, and food safety. By following these tips, travelers can minimize their risk of illness and injury and have a safe and enjoyable trip. The key takeaways from these tips include getting the necessary vaccinations, preventing malaria, practicing food and water safety, protecting against insect-borne illnesses, and staying safe in crowded areas.
What vaccinations are required for travel to Africa?
+
The required vaccinations for travel to Africa vary depending on the country and region. However, common vaccinations include yellow fever, hepatitis A, and typhoid. It’s essential to consult a healthcare professional or travel clinic to determine the necessary vaccinations for your specific trip.
How can I prevent malaria while traveling in Africa?
+
To prevent malaria, take antimalarial medication, use insecticide-treated bed nets, and wear protective clothing. Apply insect repellent regularly, especially during peak mosquito hours. It’s also essential to eliminate standing water around living areas to prevent mosquito breeding.
What are some common insect-borne illnesses in Africa?
+
Common insect-borne illnesses in Africa include malaria, dengue fever, chikungunya, and Zika virus. Take precautions to prevent these illnesses, including wearing protective clothing, applying insect repellent, and staying in air-conditioned or screened rooms.