FOB Destination Definition Explained
Introduction to FOB Destination
When it comes to shipping and logistics, understanding the terms and conditions of sale is crucial for both buyers and sellers. One of the most commonly used terms in international trade is FOB, which stands for Free on Board. In this article, we will delve into the specifics of FOB Destination, its implications, and how it affects the parties involved in a transaction.
What is FOB Destination?
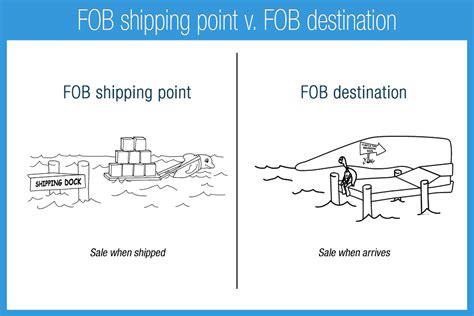
FOB Destination is a shipping term that indicates that the seller is responsible for the transportation costs and risks associated with delivering goods to the buyer’s destination. The term “FOB” itself refers to the point at which the seller’s responsibility for the goods ends, and the buyer’s responsibility begins. In the case of FOB Destination, this point is when the goods arrive at the buyer’s premises or a designated location.
Key Components of FOB Destination
To fully understand FOB Destination, it’s essential to break down its key components: * Seller’s Responsibility: The seller is responsible for arranging and paying for transportation from the point of origin to the buyer’s destination. This includes costs such as freight, insurance, and any applicable duties or taxes. * Risk of Loss: Under FOB Destination, the seller bears the risk of loss or damage to the goods until they are delivered to the buyer’s destination. If the goods are damaged or lost during transit, the seller is liable for the loss. * Delivery: The seller must ensure that the goods are delivered to the buyer’s premises or a designated location. The buyer is not responsible for arranging transportation or taking possession of the goods until they arrive at the destination.
How FOB Destination Works
Here’s a step-by-step explanation of how FOB Destination works in practice: * The seller and buyer agree on the terms of sale, including the use of FOB Destination. * The seller arranges for transportation of the goods from the point of origin to the buyer’s destination. * The seller pays for transportation costs, insurance, and any applicable duties or taxes. * The goods are shipped to the buyer’s destination, and the seller bears the risk of loss or damage during transit. * Upon arrival, the buyer takes possession of the goods and inspects them for damage or defects.
Benefits and Drawbacks of FOB Destination
Like any shipping term, FOB Destination has its benefits and drawbacks: * Benefits: + The seller has greater control over the shipping process and can choose the most cost-effective and reliable transportation options. + The buyer does not have to worry about arranging transportation or taking possession of the goods until they arrive at the destination. * Drawbacks: + The seller bears the risk of loss or damage to the goods during transit, which can be costly. + The buyer may have limited control over the shipping process and may not be able to track the goods in real-time.
Comparison with Other Shipping Terms
FOB Destination is often compared to other shipping terms, such as FOB Origin and CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight). Here’s a brief comparison: * FOB Origin: The seller is responsible for delivering the goods to the carrier at the point of origin, and the buyer bears the risk of loss or damage during transit. * CIF: The seller is responsible for paying for transportation, insurance, and freight to the buyer’s destination, but the risk of loss or damage passes to the buyer once the goods are loaded onto the ship.
| Shipping Term | Seller's Responsibility | Risk of Loss |
|---|---|---|
| FOB Destination | Transportation to buyer's destination | Seller bears risk until delivery |
| FOB Origin | Delivery to carrier at origin | Buyer bears risk during transit |
| CIF | Transportation, insurance, and freight | Risk passes to buyer once goods are loaded |
📝 Note: Understanding the differences between shipping terms is crucial for buyers and sellers to negotiate and agree on the terms of sale.
Conclusion
In summary, FOB Destination is a shipping term that places the responsibility for transportation costs and risks on the seller until the goods are delivered to the buyer’s destination. While it offers benefits such as greater control over the shipping process, it also comes with drawbacks such as the seller bearing the risk of loss or damage during transit. By understanding the key components and implications of FOB Destination, buyers and sellers can make informed decisions and negotiate the terms of sale that best suit their needs.
What is the main difference between FOB Destination and FOB Origin?
+
The main difference between FOB Destination and FOB Origin is the point at which the seller’s responsibility for the goods ends. In FOB Destination, the seller is responsible for transportation costs and risks until the goods are delivered to the buyer’s destination, while in FOB Origin, the seller is responsible only for delivering the goods to the carrier at the point of origin.
Who bears the risk of loss or damage during transit in FOB Destination?
+
In FOB Destination, the seller bears the risk of loss or damage to the goods during transit until they are delivered to the buyer’s destination.
What are the benefits of using FOB Destination in international trade?
+
The benefits of using FOB Destination include the seller having greater control over the shipping process, and the buyer not having to worry about arranging transportation or taking possession of the goods until they arrive at the destination.