Traveling
5 EU Travel Area Differences
Introduction to EU Travel Areas
The European Union (EU) is a complex entity with various agreements and zones that facilitate or restrict travel within its borders and beyond. For travelers, understanding these differences is crucial for planning trips, whether for tourism, business, or relocation. The EU Travel Area, often referred to in the context of the Schengen Area, encompasses more than just the EU, including countries that are part of the European Economic Area (EEA) and those with special agreements. This article delves into the nuances of the EU Travel Area, highlighting five key differences that travelers and residents should be aware of.
Understanding the Schengen Area
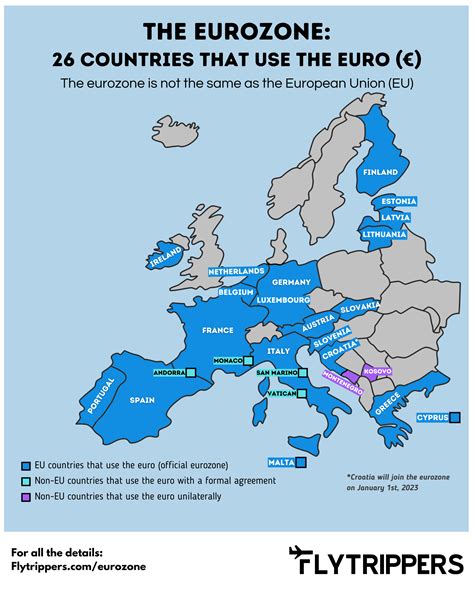
The Schengen Area is one of the most recognized components of the EU Travel Area, consisting of 26 European countries that have abolished border controls at their common borders. It functions as a single jurisdiction for international travel purposes, with a common visa policy. Countries like Germany, France, and Italy are part of the Schengen Area, making travel between these nations seamless for those who have entered the area legally. However, the Schengen Area is not the only aspect of the EU Travel Area, and its specific regulations and participating countries are just the beginning of understanding EU travel dynamics.
Differences in EU Travel Areas
There are several differences within the EU Travel Area that can affect how one plans their travel or relocation. These include:
- Schengen vs. Non-Schengen EU Countries: Not all EU countries are part of the Schengen Area. Countries like Ireland and the United Kingdom (which has since left the EU) maintained their own border controls. Understanding whether a country is part of the Schengen Area can impact visa requirements and travel restrictions.
- European Economic Area (EEA): The EEA includes all EU countries plus Iceland, Liechtenstein, and Norway. It allows for the free movement of goods, services, capital, and people between these countries. However, EEA countries that are not part of the EU, like Norway, have their own agreements regarding Schengen and other travel regulations.
- Special Agreements: Some countries have special agreements with the EU or Schengen countries that affect travel. For example, Switzerland is not an EU member but is part of the Schengen Area, allowing for passport-free travel between Switzerland and other Schengen countries.
- Visa Policies: The visa policies within the EU Travel Area can vary significantly. Some countries require visas for entry, while others do not, depending on the traveler’s nationality. The European Travel Information and Authorization System (ETIAS) is being implemented to further regulate travel for visa-free nationals, ensuring an additional layer of security.
- Border Controls and Travel Documents: The types of travel documents required (such as passports, ID cards, or visas) and the presence of border controls can vary. For EU citizens, traveling within the EU often requires only a national ID card, while non-EU citizens may need a passport and possibly a visa.
Implications for Travelers
Understanding these differences is crucial for planning a smooth and legal trip within the EU Travel Area. Researching the specific requirements for each country on your itinerary, including any necessary visas, travel documents, and health insurance, can prevent unexpected issues at borders or during your stay. Additionally, being aware of any travel restrictions or health measures in place due to global events like the COVID-19 pandemic is essential for a successful trip.
| Country/Region | Schengen Area | EU Membership | Special Agreements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Germany | Yes | Yes | No |
| France | Yes | Yes | No |
| Norway | Yes | No | EEA Member |
| Switzerland | Yes | No | Special Agreement with EU |
📝 Note: Always check the latest travel advisories and regulations before planning your trip, as policies can change frequently.
Planning Your Trip
When planning your trip within the EU Travel Area, consider the following steps: - Check Visa Requirements: Determine if you need a visa to enter any of the countries on your itinerary. - Understand Travel Documents: Ensure you have the necessary travel documents, such as a valid passport or national ID card. - Research Health and Safety: Look into any health measures or safety advisories for your destinations. - Plan for Transportation: Book your flights, trains, or other transportation methods in advance to ensure availability and the best prices. - Accommodation: Choose your accommodations wisely, considering factors like location, price, and reviews.
Final Considerations
In conclusion, navigating the EU Travel Area requires an understanding of its various components and how they interact. By recognizing the differences between Schengen and non-Schengen countries, understanding visa policies, and being aware of special agreements and travel requirements, travelers can better plan their trips and avoid potential issues. Whether you’re a seasoned traveler or embarking on your first European adventure, taking the time to research and prepare will ensure a more enjoyable and stress-free experience.
What is the Schengen Area?
+
The Schengen Area is a zone of 26 European countries that have abolished border controls at their common borders, functioning as a single jurisdiction for international travel purposes.
Do all EU countries belong to the Schengen Area?
+
No, not all EU countries are part of the Schengen Area. Some EU countries, like Ireland, have opted out, and others, like the UK, have left the EU altogether.
What is the European Economic Area (EEA)?
+
The EEA includes all EU countries plus Iceland, Liechtenstein, and Norway, allowing for the free movement of goods, services, capital, and people between these countries.