Ehrlichiosis Modes of Transmission
Introduction to Ehrlichiosis
Ehrlichiosis is a group of bacterial diseases that affect humans and animals, caused by Ehrlichia species. These bacteria are transmitted through the bites of infected ticks, making it a vector-borne disease. The most common species that cause ehrlichiosis in humans are Ehrlichia chaffeensis, Ehrlichia ewingii, and Ehrlichia muris eauclairensis. Understanding the modes of transmission is crucial for preventing and controlling the spread of this disease.
Modes of Transmission
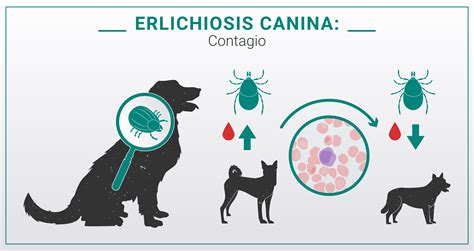
The primary mode of transmission of ehrlichiosis is through the bite of an infected tick. Ticks become infected when they feed on the blood of animals that are already infected with Ehrlichia bacteria. Once infected, the ticks can transmit the bacteria to other animals or humans through their saliva during feeding. The most common tick species that transmit ehrlichiosis are the Lone Star tick (Amblyomma americanum) and the blacklegged tick (Ixodes scapularis).
Vector-Borne Transmission
Vector-borne transmission is the primary mode of ehrlichiosis transmission. Ticks are the vectors that transmit the disease from one host to another. The transmission process involves several stages: * Tick feeding: An infected tick feeds on the blood of a host, such as a white-tailed deer or a dog. * Bacterial replication: The Ehrlichia bacteria replicate within the tick’s midgut. * Transmission to host: When the infected tick feeds on a new host, it regurgitates the bacteria into the host’s bloodstream. * Infection establishment: The bacteria establish infection in the new host, causing ehrlichiosis.
Other Modes of Transmission
While tick bites are the primary mode of transmission, other modes of transmission have been reported: * Transfusion transmission: Ehrlichiosis can be transmitted through blood transfusion from an infected donor. * Vertical transmission: There have been cases of vertical transmission, where the bacteria are transmitted from an infected mother to her child during pregnancy. * Exposure to infected animals: People who work with animals, such as veterinarians or animal handlers, may be at risk of transmission through contact with infected animals.
Prevention and Control
Preventing and controlling the spread of ehrlichiosis requires a combination of strategies: * Avoiding tick bites: Using insect repellents, wearing protective clothing, and conducting regular tick checks can help prevent tick bites. * Tick control: Controlling tick populations through the use of pesticides or other methods can help reduce the risk of transmission. * Animal control: Controlling the population of animals that can transmit the disease, such as deer, can also help reduce the risk of transmission. * Public education: Educating the public about the risks of ehrlichiosis and the importance of prevention and control measures can help reduce the incidence of the disease.
🚨 Note: Preventing tick bites is the most effective way to prevent ehrlichiosis transmission.
Epidemiology and Risk Factors
Ehrlichiosis is most commonly reported in the southern and south-central United States, where the Lone Star tick is prevalent. The disease can affect anyone, but certain groups are at higher risk: * Outdoor workers: People who work outdoors, such as landscapers or construction workers, are at higher risk of tick bites. * Animal handlers: People who work with animals, such as veterinarians or animal handlers, are at higher risk of transmission through contact with infected animals. * Immunocompromised individuals: People with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or undergoing chemotherapy, are at higher risk of severe disease.
| Species | Vector | Geographic Distribution |
|---|---|---|
| Ehrlichia chaffeensis | Lone Star tick | Southern and south-central United States |
| Ehrlichia ewingii | Lone Star tick | Southern and south-central United States |
| Ehrlichia muris eauclairensis | Blacklegged tick | Northern United States |
In summary, ehrlichiosis is a vector-borne disease transmitted primarily through the bites of infected ticks. Understanding the modes of transmission and taking preventive measures can help reduce the risk of transmission. By controlling tick populations, avoiding tick bites, and educating the public, we can work towards preventing and controlling the spread of this disease.
What is the primary mode of ehrlichiosis transmission?
+
The primary mode of ehrlichiosis transmission is through the bite of an infected tick.
What are the symptoms of ehrlichiosis?
+
The symptoms of ehrlichiosis include fever, headache, fatigue, and muscle pain.
How can I prevent ehrlichiosis transmission?
+
To prevent ehrlichiosis transmission, avoid tick bites by using insect repellents, wearing protective clothing, and conducting regular tick checks.