5 Ways Mantle Convection Works
Introduction to Mantle Convection
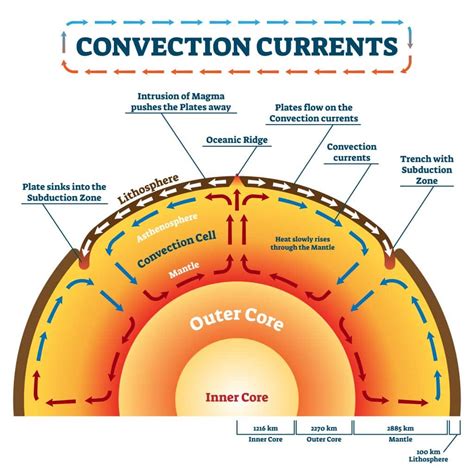
Mantle convection is a geological process that involves the movement of the Earth’s mantle, which is the layer of rock between the crust and the outer core. This process is driven by heat from the Earth’s core and is responsible for shaping the Earth’s surface over millions of years. Mantle convection is a complex process that involves the movement of hot, viscous rock over long distances, and it plays a crucial role in the Earth’s geology. In this post, we will explore the ways in which mantle convection works and its impact on the Earth’s surface.
The Process of Mantle Convection
Mantle convection is a slow process that occurs over thousands to millions of years. It involves the movement of hot, viscous rock from the Earth’s core-mantle boundary to the surface. The process can be broken down into several stages: * Heat transfer: Heat from the Earth’s core is transferred to the mantle through conduction and convection. * Thermal expansion: As the mantle rock heats up, it expands and becomes less dense than the surrounding rock. * Rising: The less dense rock rises towards the surface, creating a circulation of hot rock. * Cooling: As the rock rises, it cools and becomes more dense, eventually sinking back down to the core-mantle boundary.
5 Ways Mantle Convection Works
Mantle convection works in several ways to shape the Earth’s surface. Here are five of the most important ways: * Plate tectonics: Mantle convection drives plate tectonics, which is the movement of the Earth’s lithosphere (the outermost solid layer of the planet). The movement of the plates is responsible for the creation of mountains, volcanoes, and earthquakes. * Volcanic activity: Mantle convection is responsible for the formation of volcanoes and the eruption of magma. As the hot rock rises to the surface, it melts and forms magma, which is then erupted as lava or ash. * Earthquakes: Mantle convection is also responsible for the formation of earthquakes. As the plates move, they can get stuck, causing stress to build up. When the stress becomes too great, the plates will suddenly move, releasing the stored energy as seismic waves. * Mountain building: Mantle convection is responsible for the formation of mountains. As the plates collide, the edges of the plates are pushed upwards, forming mountains. * Sea-floor spreading: Mantle convection is also responsible for the formation of new oceanic crust. As the plates move apart, magma rises to the surface, solidifying and forming new crust.
Importance of Mantle Convection
Mantle convection is a crucial process that shapes the Earth’s surface over millions of years. It is responsible for the creation of mountains, volcanoes, and earthquakes, and it plays a key role in the Earth’s geology. Without mantle convection, the Earth’s surface would be very different, and life as we know it would not be possible.
🌎 Note: Mantle convection is a complex process that is not yet fully understood. Scientists are still studying the process to learn more about the Earth's interior and the forces that shape our planet.
Table of Mantle Convection Processes
| Process | Description |
|---|---|
| Heat transfer | Heat from the Earth’s core is transferred to the mantle through conduction and convection. |
| Thermal expansion | As the mantle rock heats up, it expands and becomes less dense than the surrounding rock. |
| Rising | The less dense rock rises towards the surface, creating a circulation of hot rock. |
| Cooling | As the rock rises, it cools and becomes more dense, eventually sinking back down to the core-mantle boundary. |
In summary, mantle convection is a complex process that shapes the Earth’s surface over millions of years. It is responsible for the creation of mountains, volcanoes, and earthquakes, and it plays a key role in the Earth’s geology. By understanding mantle convection, we can gain insights into the Earth’s interior and the forces that shape our planet.
What is mantle convection?
+
Mantle convection is a geological process that involves the movement of the Earth’s mantle, which is the layer of rock between the crust and the outer core.
What drives mantle convection?
+
Mantle convection is driven by heat from the Earth’s core.
What are the effects of mantle convection?
+
Mantle convection is responsible for the creation of mountains, volcanoes, and earthquakes, and it plays a key role in the Earth’s geology.