5 Ways Override Policy
Introduction to Override Policy
In various systems, especially those involving technology, finance, or management, the concept of an override policy is crucial. An override policy refers to a set of rules or procedures that allow for exceptions to standard policies under specific circumstances. These exceptions are typically made to accommodate unique situations, resolve conflicts, or mitigate potential losses. The ability to override standard policies is a powerful tool, but it must be used judiciously to avoid abuse or inconsistencies.
Understanding the Need for Override Policies
Override policies are essential in environments where rigid adherence to rules could lead to undesirable outcomes. For instance, in financial transactions, an override might be necessary to facilitate a large, legitimate transfer that exceeds usual limits. Similarly, in software development, overriding certain constraints can help in testing or debugging processes. However, the implementation and management of override policies require careful consideration to ensure they serve their intended purpose without compromising the system’s integrity.
5 Ways to Override Policy Effectively
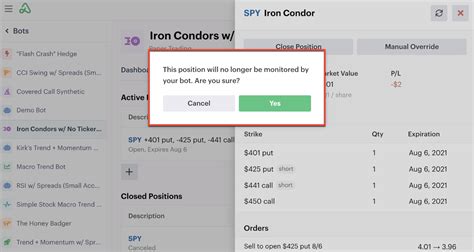
Implementing an effective override policy involves several key considerations: - Clear Definition of Circumstances: The policy should clearly outline under what circumstances an override is permissible. This could include emergency situations, large financial transactions, or specific business needs. - Authorization and Approval: There should be a clear hierarchy of authorization for overrides. This ensures that decisions are made at the appropriate level and are properly documented. - Documentation and Auditing: All overrides should be thoroughly documented, including the reason for the override, the individuals involved in the decision, and the outcome. Regular auditing of overrides helps in identifying patterns of abuse or areas where the policy might need adjustment. - Limitations and Constraints: To prevent abuse, override policies should include specific limitations and constraints. For example, the value of transactions that can be overridden, the frequency of overrides, or the specific conditions under which overrides are allowed. - Review and Update: Override policies should be subject to periodic review. This helps in ensuring that the policy remains relevant, effective, and aligned with the organization’s goals and regulatory requirements.
Benefits of a Well-Implemented Override Policy
A well-designed and implemented override policy offers several benefits: - Flexibility: It provides the necessary flexibility to deal with unusual or unexpected situations. - Risk Management: By allowing for overrides under controlled circumstances, organizations can better manage risks associated with rigid policy adherence. - Efficiency: Overrides can help in expediting processes or resolving issues quickly, thus improving operational efficiency. - Compliance: A clear override policy helps in demonstrating compliance with regulatory requirements, as it shows a proactive approach to managing exceptions.
Challenges and Considerations
While override policies are beneficial, there are challenges and considerations: - Abuse: The potential for abuse is a significant concern. Without proper controls, overrides can be used inappropriately, leading to financial losses or breaches of trust. - Complexity: Managing override policies can add complexity to systems and processes, requiring additional resources for oversight and management. - Security: In technological systems, overrides can introduce security vulnerabilities if not properly secured and monitored.
🚨 Note: Implementing an override policy requires a balance between flexibility and control. Regular monitoring and auditing are essential to prevent abuse and ensure the policy's effectiveness.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, override policies are a critical component of flexible and responsive systems, whether in technology, finance, or management. By understanding the need for such policies, implementing them effectively, and being aware of the potential challenges, organizations can leverage overrides to improve efficiency, manage risks, and adapt to changing circumstances. As systems and technologies continue to evolve, the role of override policies will likely become even more significant, necessitating ongoing review and refinement to ensure they remain effective and secure.
What is the primary purpose of an override policy?
+
The primary purpose of an override policy is to provide a structured approach to making exceptions to standard rules or policies under specific circumstances, ensuring flexibility and adaptability in operations.
How often should override policies be reviewed and updated?
+
Override policies should be subject to periodic review, ideally on an annual basis or as needed based on changes in the organization, technology, or regulatory environment. This ensures the policy remains effective, relevant, and compliant with current standards and laws.
What are the key elements of an effective override policy?
+
An effective override policy includes clear definitions of when overrides are allowed, a hierarchy of authorization, thorough documentation and auditing, specific limitations and constraints, and a process for regular review and update.