5 Ways Campylobacter Jejuni Travels
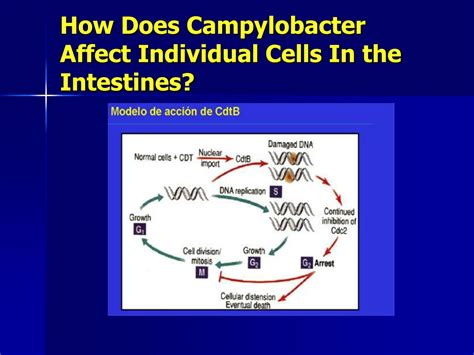
Introduction to Campylobacter Jejuni
Campylobacter jejuni is a gram-negative bacterium that is one of the most common causes of gastroenteritis in humans. It is a zoonotic pathogen, meaning it can be transmitted between animals and humans. The bacterium is typically found in the gastrointestinal tract of animals, such as poultry and cattle, and can be spread to humans through various routes. In this article, we will explore the 5 ways Campylobacter jejuni travels and highlight the importance of proper hygiene and food safety practices to prevent its transmission.
Route 1: Contaminated Food and Water
One of the primary ways Campylobacter jejuni travels is through contaminated food and water. The bacterium can be present in raw or undercooked poultry, unpasteurized dairy products, and contaminated water. When humans consume these contaminated products, they can become infected with the bacterium. Raw vegetables and fruits can also become contaminated with Campylobacter jejuni if they come into contact with infected animal feces or contaminated water.
Route 2: Direct Contact with Infected Animals
Another way Campylobacter jejuni travels is through direct contact with infected animals. People who work with animals, such as farmers and veterinarians, are at a higher risk of becoming infected with the bacterium. Pets can also carry Campylobacter jejuni, and people can become infected if they do not practice proper hygiene when handling their pets’ waste.
Route 3: Person-to-Person Transmission
Campylobacter jejuni can also be transmitted from person-to-person. This can occur when an infected person does not practice proper hygiene, such as not washing their hands after using the bathroom or before preparing food. Daycare centers and other settings where people are in close proximity can be breeding grounds for the transmission of Campylobacter jejuni.
Route 4: Contaminated Environment
The bacterium can also travel through a contaminated environment. Campylobacter jejuni can survive in water and soil for extended periods, and people can become infected if they come into contact with these contaminated environments. Floods and other natural disasters can also spread the bacterium, as they can contaminate water sources and soil.
Route 5: Insects and Vectors
Finally, Campylobacter jejuni can travel through insects and vectors. Flies and other insects can carry the bacterium on their bodies and transfer it to food and surfaces. Ticks and other vectors can also spread the bacterium, although this is less common.
🚨 Note: It is essential to practice proper hygiene and food safety to prevent the transmission of Campylobacter jejuni.
In summary, Campylobacter jejuni is a highly infectious bacterium that can travel through various routes, including contaminated food and water, direct contact with infected animals, person-to-person transmission, contaminated environments, and insects and vectors. By understanding these routes, we can take steps to prevent the transmission of the bacterium and reduce the risk of infection.
To prevent the transmission of Campylobacter jejuni, it is essential to: * Practice proper hygiene, such as washing hands regularly * Handle food safely, including cooking poultry to the recommended internal temperature * Avoid consuming unpasteurized dairy products and raw or undercooked poultry * Prevent cross-contamination of food and surfaces * Keep environments clean, including regularly cleaning and disinfecting surfaces and utensils
By following these steps, we can reduce the risk of Campylobacter jejuni infection and prevent the spread of this highly infectious bacterium.
The main points to remember are: * Campylobacter jejuni is a highly infectious bacterium that can cause gastroenteritis * The bacterium can travel through various routes, including contaminated food and water, direct contact with infected animals, person-to-person transmission, contaminated environments, and insects and vectors * Proper hygiene and food safety practices are essential to prevent the transmission of the bacterium * By understanding the routes of transmission and taking steps to prevent them, we can reduce the risk of infection and prevent the spread of Campylobacter jejuni
In final thoughts, the transmission of Campylobacter jejuni can be prevented by practicing proper hygiene and food safety. It is crucial to understand the routes of transmission and take steps to prevent them. By doing so, we can reduce the risk of infection and prevent the spread of this highly infectious bacterium.
What is Campylobacter jejuni?
+
Campylobacter jejuni is a gram-negative bacterium that is one of the most common causes of gastroenteritis in humans.
How is Campylobacter jejuni transmitted?
+
Campylobacter jejuni can be transmitted through contaminated food and water, direct contact with infected animals, person-to-person transmission, contaminated environments, and insects and vectors.
How can I prevent the transmission of Campylobacter jejuni?
+
To prevent the transmission of Campylobacter jejuni, it is essential to practice proper hygiene, handle food safely, avoid consuming unpasteurized dairy products and raw or undercooked poultry, prevent cross-contamination of food and surfaces, and keep environments clean.
What are the symptoms of Campylobacter jejuni infection?
+
The symptoms of Campylobacter jejuni infection can include diarrhea, abdominal cramps, fever, and vomiting. In severe cases, the infection can lead to life-threatening complications, such as sepsis and meningitis.
How is Campylobacter jejuni treated?
+
Campylobacter jejuni infection is typically treated with antibiotics, such as azithromycin or ciprofloxacin. In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary to manage complications and prevent dehydration.