Hepatitis A Virus Travel Methods
Understanding Hepatitis A Virus and Its Travel-Related Risks
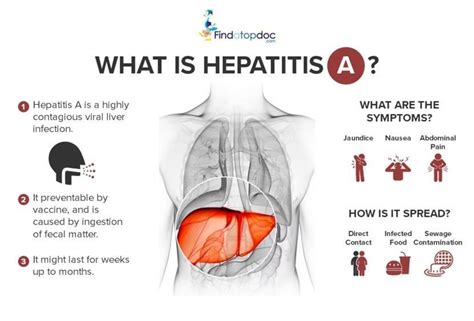
The Hepatitis A virus (HAV) is a highly contagious liver infection that can be spread through contaminated food, water, and close contact with an infected person. When traveling to areas with poor sanitation and inadequate hygiene, the risk of contracting Hepatitis A increases significantly. This post will delve into the specifics of how Hepatitis A virus is transmitted, especially in the context of travel, and what measures can be taken to prevent infection.
Transmission Methods of Hepatitis A Virus
Hepatitis A virus is primarily spread through the fecal-oral route. This means that the virus is present in the stool of infected individuals and can be ingested by others through contaminated food, water, or direct contact. Key methods of transmission include: - Contaminated Food and Water: Consuming food or water that has been contaminated with the feces of an infected person. - Close Contact: Direct contact with an infected person, such as through touching or shaking hands, and then touching one’s mouth. - Sexual Contact: Certain sexual practices can also spread the virus. - Contaminated Surfaces and Objects: Touching surfaces or objects that have come into contact with the virus and then touching one’s mouth.
Travel Destinations with High Risk of Hepatitis A
Certain regions and countries have a higher prevalence of Hepatitis A due to inadequate sanitation, poor hygiene practices, and insufficient access to clean water. Travelers to these areas are at a greater risk of infection. Some of these destinations include: - Parts of Africa - Asia (except for Japan and some areas of the Middle East) - Central and South America - Eastern Europe (some areas) - Pacific Islands (some areas)
Prevention Measures for Travelers
To minimize the risk of contracting Hepatitis A while traveling, several preventative measures can be taken: - Vaccination: The most effective way to prevent Hepatitis A infection is through vaccination. Travelers should consider getting vaccinated at least two weeks before their trip. - Practice Good Hygiene: Frequent handwashing with soap and clean water, especially after using the bathroom and before eating. - Avoid Contaminated Food and Water: Avoid eating undercooked or raw foods, especially shellfish, and drink bottled or filtered water. - Avoid Close Contact: Be mindful of personal space and hygiene when interacting with locals.
Symptoms and Treatment of Hepatitis A
Recognizing the symptoms of Hepatitis A is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment. Common symptoms include: - Fatigue - Nausea and Vomiting - Abdominal Pain - Loss of Appetite - Dark Urine and Pale Stools - Yellowing of the Skin and Eyes (Jaundice) While there is no specific treatment for Hepatitis A, symptoms can be managed, and in severe cases, hospitalization may be required to prevent complications.
Protecting Yourself and Others
Protecting oneself from Hepatitis A also involves protecting others. If infected, it’s essential to: - Inform Close Contacts: Let friends, family, and sexual partners know about the infection so they can take preventative measures. - Practice Isolation: Avoid preparing food for others and maintain good personal hygiene to prevent the spread.
| Preventative Measure | Description |
|---|---|
| Vaccination | Get vaccinated at least two weeks before traveling to high-risk areas. |
| Good Hygiene | Wash hands frequently with soap and clean water. |
| Avoid Contaminated Food and Water | Eat cooked foods and drink bottled or filtered water. |
🚨 Note: Always consult a healthcare professional before traveling to discuss the risk of Hepatitis A and other travel-related illnesses, and to determine the best course of prevention based on your specific travel plans and health status.
In summary, understanding the transmission methods of Hepatitis A virus, being aware of high-risk travel destinations, and taking preventative measures such as vaccination and practicing good hygiene are key to minimizing the risk of infection. By taking these steps, travelers can enjoy their trips while protecting their health and the health of those around them. The importance of being informed and prepared cannot be overstated, especially when it comes to preventing the spread of contagious diseases like Hepatitis A. By adopting a proactive approach to health and hygiene, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of contracting Hepatitis A and ensure a safe and enjoyable travel experience.
What is the primary method of Hepatitis A transmission?
+
The primary method of Hepatitis A transmission is through the fecal-oral route, where the virus is ingested through contaminated food, water, or direct contact with an infected person.
Which travel destinations have a high risk of Hepatitis A?
+
Areas with inadequate sanitation and hygiene, such as parts of Africa, Asia (except for Japan and some Middle Eastern areas), Central and South America, Eastern Europe (some areas), and Pacific Islands (some areas), have a higher prevalence of Hepatitis A.
How can travelers prevent Hepatitis A infection?
+
Travelers can prevent Hepatitis A infection by getting vaccinated, practicing good hygiene (frequent handwashing), avoiding contaminated food and water, and avoiding close contact with potentially infected individuals.