Microsporidia Travel Methods
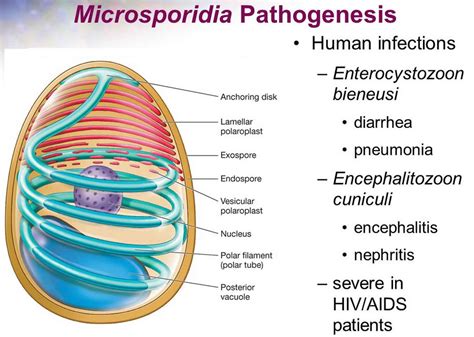
Introduction to Microsporidia
Microsporidia are a group of obligate intracellular parasites that infect a wide range of hosts, including animals, plants, and other microorganisms. These parasites have been found in almost every environment, from freshwater to marine ecosystems, and even in the human body. One of the most fascinating aspects of microsporidia is their ability to travel and infect new hosts. In this blog post, we will explore the different methods that microsporidia use to travel and infect new hosts.
Spore-Based Travel
Microsporidia produce resistant spores that can survive outside of a host for extended periods. These spores are the primary means by which microsporidia travel and infect new hosts. The spores are highly resistant to environmental stresses, such as extreme temperatures, UV radiation, and desiccation, which allows them to survive in a variety of environments. When a spore comes into contact with a suitable host, it germinates and infects the host cell.
Waterborne Transmission
One of the primary methods by which microsporidia travel is through waterborne transmission. The spores can be released into the water through the feces of infected hosts or through the decay of infected tissues. The spores can then be transported through the water to new locations, where they can infect new hosts. This method of transmission is particularly important in aquatic ecosystems, where microsporidia can infect a wide range of hosts, including fish, crustaceans, and other invertebrates.
Airborne Transmission
In addition to waterborne transmission, microsporidia can also be transmitted through the air. The spores can become airborne through the disturbance of contaminated soil or water, or through the movement of infected hosts. Once airborne, the spores can be transported to new locations, where they can infect new hosts. This method of transmission is particularly important in terrestrial ecosystems, where microsporidia can infect a wide range of hosts, including animals and plants.
Vector-Based Transmission
Microsporidia can also be transmitted through vectors, such as insects and other arthropods. The spores can be ingested by the vector, which can then transport the spores to new locations and infect new hosts. This method of transmission is particularly important in ecosystems where vectors are abundant, such as in tropical and subtropical regions.
Horizontal Transmission
In addition to the methods mentioned above, microsporidia can also be transmitted through horizontal transmission, which occurs when an infected host comes into contact with an uninfected host. This method of transmission is particularly important in dense populations, where hosts are in close proximity to each other.
🌟 Note: Microsporidia can also be transmitted through vertical transmission, which occurs when an infected host passes the parasite to its offspring.
Travel Methods Summary
In summary, microsporidia use a variety of methods to travel and infect new hosts, including: * Spore-based travel * Waterborne transmission * Airborne transmission * Vector-based transmission * Horizontal transmission
| Travel Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Spore-based travel | Microsporidia produce resistant spores that can survive outside of a host for extended periods. |
| Waterborne transmission | Microsporidia can be transmitted through water, where they can infect new hosts. |
| Airborne transmission | Microsporidia can become airborne and be transported to new locations, where they can infect new hosts. |
| Vector-based transmission | Microsporidia can be transmitted through vectors, such as insects and other arthropods. |
| Horizontal transmission | Microsporidia can be transmitted through contact between infected and uninfected hosts. |
Microsporidia are highly adaptable parasites that can infect a wide range of hosts. Their ability to travel and infect new hosts is a key factor in their success, and understanding these methods is essential for developing effective control strategies. By recognizing the different travel methods used by microsporidia, we can better appreciate the complexity and diversity of these fascinating parasites.
What is the primary method of transmission for microsporidia?
+
The primary method of transmission for microsporidia is through spore-based travel, where the parasites produce resistant spores that can survive outside of a host for extended periods.
Can microsporidia be transmitted through water?
+
Yes, microsporidia can be transmitted through water, where they can infect new hosts. This method of transmission is particularly important in aquatic ecosystems.
What is the role of vectors in the transmission of microsporidia?
+
Vectors, such as insects and other arthropods, can play a role in the transmission of microsporidia by ingesting the spores and transporting them to new locations, where they can infect new hosts.