Traveling
Microsporidia Travel Methods
Introduction to Microsporidia
Microsporidia are a group of obligate intracellular parasites that infect a wide range of hosts, including animals, plants, and other microorganisms. These parasites have been found in almost every environment, from freshwater to marine ecosystems, and even in the bodies of humans. One of the most fascinating aspects of microsporidia is their ability to travel and infect new hosts. In this blog post, we will explore the different methods that microsporidia use to travel and spread to new hosts.
Methods of Travel
Microsporidia have evolved several strategies to travel and infect new hosts. Some of the most common methods include: * Contaminated water: Microsporidia can contaminate water sources, such as rivers, lakes, and oceans, and be ingested by new hosts. * Infected insects: Microsporidia can infect insects, such as mosquitoes and flies, which can then transmit the parasite to new hosts through bites or contact. * Contaminated food: Microsporidia can contaminate food sources, such as fish and other seafood, and be ingested by new hosts. * Direct contact: Microsporidia can be transmitted through direct contact with an infected host, such as through touching or rubbing against an infected animal.
Life Cycle of Microsporidia
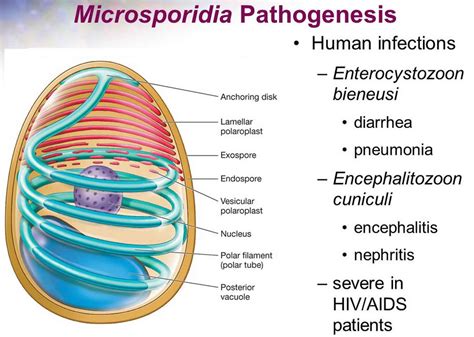
The life cycle of microsporidia is complex and involves several stages. The parasite begins its life cycle as a spore, which is the infectious stage of the parasite. The spore is ingested by a new host, where it germinates and releases a polar tube that infects the host cell. The parasite then multiplies within the host cell, producing more spores that can be released into the environment to infect new hosts.
Travel Through the Environment
Microsporidia can travel through the environment in several ways, including: * Water currents: Microsporidia can be carried by water currents, such as rivers and oceans, to new locations. * Wind: Microsporidia can be carried by wind, such as through dust and other airborne particles, to new locations. * Animals: Microsporidia can be carried by animals, such as birds and other migratory species, to new locations.
🚨 Note: Microsporidia can survive for long periods of time outside of a host, allowing them to travel and infect new hosts even after the original host has died.
Impact of Microsporidia on Hosts
Microsporidia can have a significant impact on their hosts, including: * Disease: Microsporidia can cause disease in their hosts, such as microsporidiosis, which can lead to symptoms such as diarrhea, weight loss, and respiratory problems. * Death: Microsporidia can cause death in their hosts, particularly in immunocompromised individuals. * Reduced fertility: Microsporidia can reduce fertility in their hosts, making it difficult for them to reproduce.
Prevention and Control
Preventing and controlling the spread of microsporidia is crucial to reducing the impact of these parasites on their hosts. Some methods of prevention and control include: * Proper water treatment: Treating water sources to remove microsporidia can help prevent the spread of the parasite. * Use of protective gear: Using protective gear, such as gloves and masks, can help prevent the spread of microsporidia through direct contact. * Good hygiene practices: Practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands regularly, can help prevent the spread of microsporidia.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, microsporidia are a fascinating group of parasites that have evolved several strategies to travel and infect new hosts. Understanding the methods of travel and the life cycle of microsporidia is crucial to preventing and controlling the spread of these parasites. Future research should focus on developing effective methods of prevention and control, as well as improving our understanding of the biology and ecology of microsporidia.
What are microsporidia?
+
Microsporidia are a group of obligate intracellular parasites that infect a wide range of hosts, including animals, plants, and other microorganisms.
How do microsporidia travel?
+
Microsporidia can travel through contaminated water, infected insects, contaminated food, and direct contact with an infected host.
What is the impact of microsporidia on hosts?
+
Microsporidia can cause disease, death, and reduced fertility in their hosts, particularly in immunocompromised individuals.