5 Ways Plasmodium Travels
Introduction to Plasmodium and Its Life Cycle
Plasmodium, the parasite responsible for malaria, has a complex life cycle that involves two main hosts: the human and the mosquito. The parasite’s ability to travel between these hosts is crucial for its survival and propagation. In this blog post, we will explore the five ways Plasmodium travels, highlighting the key stages of its life cycle and the mechanisms it uses to infect and spread between hosts.
The Life Cycle of Plasmodium
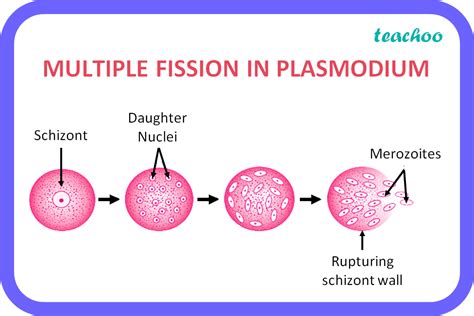
The life cycle of Plasmodium involves several stages, including the sporozoite, merozoite, trophozoite, schizont, and gametocyte stages. The sporozoite stage is the infectious stage, where the parasite is transmitted from the mosquito to the human host through a bite. The merozoite stage is the stage where the parasite infects red blood cells, causing the disease symptoms. The trophozoite and schizont stages are the stages where the parasite multiplies and matures, respectively. The gametocyte stage is the stage where the parasite is transmitted from the human host back to the mosquito.
5 Ways Plasmodium Travels
The following are the five ways Plasmodium travels: * Through the bite of an infected mosquito: This is the primary mode of transmission, where an infected mosquito bites a human, injecting the sporozoite stage of the parasite into the person’s bloodstream. * Through blood transfusion: Plasmodium can also be transmitted through blood transfusion, where infected blood is transfused into a non-infected person. * Through organ transplantation: In rare cases, Plasmodium can be transmitted through organ transplantation, where an infected organ is transplanted into a non-infected person. * Through mother-to-child transmission: Plasmodium can also be transmitted from an infected mother to her child during pregnancy or childbirth. * Through contaminated needles and syringes: In some cases, Plasmodium can be transmitted through contaminated needles and syringes, where infected blood is injected into a non-infected person.
Mechanisms of Plasmodium Travel
Plasmodium uses several mechanisms to travel between hosts, including: * Mosquito salivary glands: The parasite uses the mosquito’s salivary glands to infect the human host. * Human skin: The parasite uses the human skin as a portal of entry, where it infects the bloodstream. * Bloodstream: The parasite uses the bloodstream to travel to the liver, where it infects liver cells. * Liver cells: The parasite uses liver cells to mature and multiply, before infecting red blood cells.
💡 Note: Understanding the mechanisms of Plasmodium travel is crucial for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies.
Prevention and Treatment Strategies
Prevention and treatment strategies for Plasmodium infection include: * Using insecticide-treated bed nets: This can help prevent mosquito bites and reduce the risk of transmission. * Wearing protective clothing: Wearing protective clothing, such as long-sleeved shirts and pants, can help prevent mosquito bites. * Using antimalarial medications: Antimalarial medications, such as chloroquine and mefloquine, can help treat and prevent Plasmodium infection. * Implementing vector control measures: Vector control measures, such as eliminating mosquito breeding sites and using insecticides, can help reduce the risk of transmission.
| Prevention Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Using insecticide-treated bed nets | This can help prevent mosquito bites and reduce the risk of transmission. |
| Wearing protective clothing | Wearing protective clothing, such as long-sleeved shirts and pants, can help prevent mosquito bites. |
| Using antimalarial medications | Antimalarial medications, such as chloroquine and mefloquine, can help treat and prevent Plasmodium infection. |
| Implementing vector control measures | Vector control measures, such as eliminating mosquito breeding sites and using insecticides, can help reduce the risk of transmission. |
In summary, Plasmodium travels through several mechanisms, including the bite of an infected mosquito, blood transfusion, organ transplantation, mother-to-child transmission, and contaminated needles and syringes. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies. By using insecticide-treated bed nets, wearing protective clothing, using antimalarial medications, and implementing vector control measures, we can reduce the risk of Plasmodium infection and ultimately eliminate the disease.
What is the primary mode of Plasmodium transmission?
+
The primary mode of Plasmodium transmission is through the bite of an infected mosquito.
Can Plasmodium be transmitted through blood transfusion?
+
Yes, Plasmodium can be transmitted through blood transfusion, where infected blood is transfused into a non-infected person.
What are some prevention strategies for Plasmodium infection?
+
Prevention strategies for Plasmodium infection include using insecticide-treated bed nets, wearing protective clothing, using antimalarial medications, and implementing vector control measures.