How Sound Travels Through Air
Introduction to Sound Waves
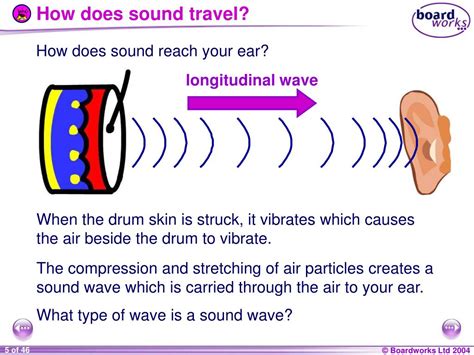
Sound is a form of energy that is produced by vibrations. When an object vibrates, it creates a disturbance in the air particles around it, causing them to oscillate back and forth. These oscillations, or sound waves, are what allow us to hear the sound. Sound waves are a type of mechanical wave, which means they require a physical medium to travel through. In this case, the medium is air.
The Process of Sound Transmission
The process of sound transmission through air is complex, but it can be broken down into several key steps: * Vibration: An object vibrates, creating a disturbance in the air particles around it. * Compression: The vibrating object compresses the air particles, causing them to become denser. * Rarefaction: The compressed air particles then expand, becoming less dense. * Wave Propagation: The cycle of compression and rarefaction continues, allowing the sound wave to propagate through the air.
Factors Affecting Sound Travel
There are several factors that can affect how sound travels through air, including: * Temperature: Temperature affects the speed of sound, with sound traveling faster in warmer temperatures. * Humidity: Humidity can affect the speed of sound, with sound traveling faster in more humid environments. * Air Pressure: Changes in air pressure can affect the speed of sound, with sound traveling faster at higher pressures. * Obstacles: Physical obstacles, such as buildings or trees, can block or absorb sound waves, affecting how they travel.
The Speed of Sound
The speed of sound in air is approximately 343 meters per second at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. This speed can vary depending on the factors mentioned earlier. The speed of sound is an important factor in understanding how sound travels, as it determines how quickly sound waves can propagate through the air.
Sound Wave Characteristics
Sound waves have several characteristics that are important to understand, including: * Frequency: The frequency of a sound wave determines its pitch, with higher frequencies producing higher pitches. * Amplitude: The amplitude of a sound wave determines its loudness, with higher amplitudes producing louder sounds. * Wavelength: The wavelength of a sound wave determines its speed, with shorter wavelengths producing higher speeds.
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Frequency | Determines pitch |
| Amplitude | Determines loudness |
| Wavelength | Determines speed |
📝 Note: Understanding the characteristics of sound waves is crucial in understanding how sound travels through air.
Applications of Sound Travel
The understanding of how sound travels through air has numerous applications in various fields, including: * Music: Understanding how sound travels is essential in music production and acoustic design. * Communication: The study of sound travel is crucial in the development of communication systems, such as telephones and radios. * Medicine: The understanding of sound travel is used in medical imaging techniques, such as ultrasound.
In summary, sound travels through air as a result of vibrations creating disturbances in air particles. The process of sound transmission involves compression, rarefaction, and wave propagation. Factors such as temperature, humidity, air pressure, and obstacles can affect how sound travels. Understanding the characteristics of sound waves, including frequency, amplitude, and wavelength, is essential in understanding how sound travels. The applications of sound travel are diverse and have a significant impact on various fields.
What is the speed of sound in air?
+
The speed of sound in air is approximately 343 meters per second at room temperature and atmospheric pressure.
What factors affect sound travel?
+
Temperature, humidity, air pressure, and obstacles can affect how sound travels through air.
What are the characteristics of sound waves?
+
Sound waves have characteristics such as frequency, amplitude, and wavelength, which determine their pitch, loudness, and speed.