Streptococcus Pneumoniae Travel Methods
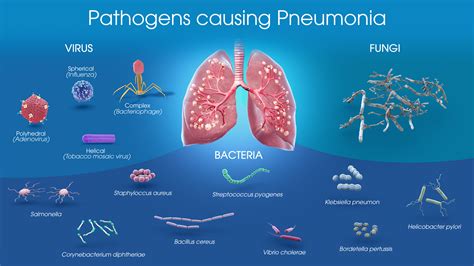
Introduction to Streptococcus Pneumoniae
Streptococcus pneumoniae, also known as pneumococcus, is a type of bacteria that can cause a range of diseases, including pneumonia, meningitis, and sepsis. This bacterium is commonly found in the throat and nose of healthy individuals, but it can become pathogenic under certain conditions. Streptococcus pneumoniae is a significant public health concern, particularly among young children, older adults, and people with weakened immune systems.
Transmission Methods of Streptococcus Pneumoniae
The primary mode of transmission of Streptococcus pneumoniae is through respiratory droplets that are expelled when an infected person coughs or sneezes. These droplets can be inhaled by others, allowing the bacteria to colonize their respiratory tract. The bacteria can also be spread through close contact with an infected person, such as touching or sharing utensils. Additionally, Streptococcus pneumoniae can be transmitted through contaminated surfaces or objects that have come into contact with respiratory secretions.
Travel Methods and the Spread of Streptococcus Pneumoniae
The widespread use of air travel has increased the potential for the global spread of infectious diseases, including Streptococcus pneumoniae. When infected individuals travel, they can carry the bacteria to new locations, potentially introducing it to susceptible populations. The risk of transmission is particularly high in confined spaces such as airplanes, where people are in close proximity to each other and may be more likely to share respiratory droplets.
Some of the key factors that contribute to the spread of Streptococcus pneumoniae through travel include: * Density of population: Areas with high population densities, such as cities or tourist destinations, can facilitate the spread of the bacteria. * Global connectivity: The ease of international travel has created a global network that allows infectious diseases to spread quickly across the world. * Vaccination rates: Low vaccination rates in certain populations or regions can increase the risk of Streptococcus pneumoniae transmission. * Climate and weather conditions: Climate and weather conditions, such as cold temperatures or humidity, can affect the survival and transmission of the bacteria.
Prevention and Control Measures
To prevent the spread of Streptococcus pneumoniae, it is essential to implement effective control measures, including: * Vaccination: Vaccination is the most effective way to prevent Streptococcus pneumoniae infections. There are several types of pneumococcal vaccines available, including conjugate and polysaccharide vaccines. * Respiratory hygiene: Practicing good respiratory hygiene, such as covering the mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing, can help reduce the transmission of the bacteria. * Hand hygiene: Regular hand washing with soap and water can help prevent the spread of Streptococcus pneumoniae. * Avoiding close contact: Avoiding close contact with individuals who are infected with Streptococcus pneumoniae can help reduce the risk of transmission.
| Vaccine Type | Age Group | Number of Doses |
|---|---|---|
| PCV13 (Prevnar 13) | Infants and young children | 4 doses |
| PPSV23 (Pneumovax 23) | Adults 65 years and older | 1 dose |
| PCV20 (Prevnar 20) | Adults 18 years and older | 1 dose |
🚨 Note: The vaccine schedule may vary depending on the country, region, or individual health status. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized vaccination recommendations.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, Streptococcus pneumoniae is a significant public health concern that can be spread through various travel methods. To prevent the spread of this bacterium, it is essential to implement effective control measures, including vaccination, respiratory hygiene, hand hygiene, and avoiding close contact with infected individuals. Further research is needed to develop more effective vaccines and to improve our understanding of the transmission dynamics of Streptococcus pneumoniae.
As we move forward, it is crucial to prioritize global health security and to strengthen our ability to respond to emerging infectious disease threats. This can be achieved through international collaboration, investing in vaccine research and development, and improving public health infrastructure. By working together, we can reduce the burden of Streptococcus pneumoniae and protect vulnerable populations from this serious and potentially life-threatening disease.
What is the most effective way to prevent Streptococcus pneumoniae infections?
+
Vaccination is the most effective way to prevent Streptococcus pneumoniae infections. There are several types of pneumococcal vaccines available, including conjugate and polysaccharide vaccines.
How is Streptococcus pneumoniae transmitted?
+
Streptococcus pneumoniae is primarily transmitted through respiratory droplets that are expelled when an infected person coughs or sneezes. The bacteria can also be spread through close contact with an infected person or through contaminated surfaces or objects.
What are the risk factors for Streptococcus pneumoniae infections?
+
The risk factors for Streptococcus pneumoniae infections include age (young children and older adults), weakened immune system, and certain underlying medical conditions, such as heart disease or lung disease.