Sound Travel Speed
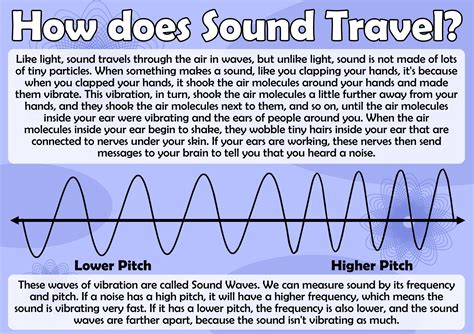
Introduction to Sound Travel Speed
The speed at which sound travels is a fundamental concept in physics, and it plays a crucial role in various fields, including music, communication, and even medical imaging. Sound travel speed, also known as the speed of sound, refers to the rate at which sound waves propagate through a medium, such as air, water, or solids. In this blog post, we will delve into the world of sound travel speed, exploring its definition, factors that affect it, and its applications in different areas.
Definition and Factors Affecting Sound Travel Speed
The speed of sound is defined as the distance traveled by a sound wave per unit time, typically measured in meters per second (m/s). The speed of sound in air at room temperature and atmospheric pressure is approximately 343 m/s. However, this value can vary depending on several factors, including: * Temperature: An increase in temperature results in an increase in sound travel speed. * Pressure: An increase in pressure leads to an increase in sound travel speed. * Humidity: High humidity can slightly increase sound travel speed. * Medium: Sound travels faster in solids and liquids than in gases.
Applications of Sound Travel Speed
The concept of sound travel speed has numerous applications in various fields, including: * Music and Acoustics: Understanding sound travel speed is essential for designing concert halls, recording studios, and musical instruments. * Communication: Sound travel speed plays a critical role in the development of communication systems, such as telephones, radios, and sonar technology. * Medical Imaging: Sound travel speed is used in medical imaging techniques, such as ultrasound and echocardiography, to create images of internal organs and tissues. * Seismology: Sound travel speed is used to study seismic waves and understand the structure of the Earth’s interior.
Measurement of Sound Travel Speed
Measuring sound travel speed can be done using various methods, including: * Time-of-Flight Method: This method involves measuring the time it takes for a sound wave to travel between two points. * Frequency Method: This method involves measuring the frequency of a sound wave and using it to calculate the sound travel speed. * Interferometry Method: This method involves using interference patterns to measure the sound travel speed.
📝 Note: The measurement of sound travel speed is crucial in various applications, and the choice of method depends on the specific requirements and conditions.
Table of Sound Travel Speed in Different Mediums
The following table shows the sound travel speed in different mediums:
| Medium | Sound Travel Speed (m/s) |
|---|---|
| Air (room temperature and atmospheric pressure) | 343 |
| Water | 1480 |
| Steel | 6100 |
| Human Body | 1540 |
In summary, sound travel speed is a vital concept that has numerous applications in various fields. Understanding the factors that affect sound travel speed and measuring it accurately is essential for designing and developing systems that rely on sound waves. By recognizing the importance of sound travel speed, we can appreciate the complexity and beauty of the physical world around us.
What is the speed of sound in air at room temperature and atmospheric pressure?
+
The speed of sound in air at room temperature and atmospheric pressure is approximately 343 m/s.
What are the factors that affect sound travel speed?
+
The factors that affect sound travel speed include temperature, pressure, humidity, and the medium through which the sound wave travels.
What are some of the applications of sound travel speed?
+
Some of the applications of sound travel speed include music and acoustics, communication, medical imaging, and seismology.