Traveling
CDC Immunization Guidelines
Introduction to CDC Immunization Guidelines
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) plays a crucial role in protecting public health and safety in the United States. One of the key areas of focus for the CDC is immunization. Immunization is the process by which a person is made immune or resistant to an infectious disease, typically by the administration of a vaccine. The CDC provides guidelines for immunization to help healthcare professionals and the general public understand the recommended vaccines, dosages, and schedules for various age groups and populations.
Importance of Immunization
Immunization is essential for preventing the spread of infectious diseases and protecting individuals, especially those who are most vulnerable, such as the elderly, young children, and people with weakened immune systems. Vaccines help to build herd immunity, which occurs when a significant portion of a community becomes immune to a disease, making its spread from person to person unlikely. This is crucial for preventing outbreaks and protecting those who cannot receive vaccines due to medical conditions.
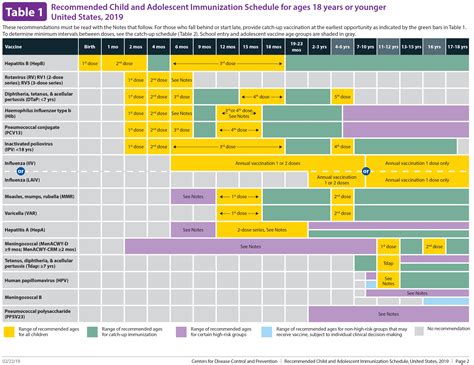
CDC Recommended Immunization Schedule
The CDC recommends a schedule of vaccines for individuals from birth through adulthood. This schedule is designed to provide protection against serious and potentially life-threatening diseases. The schedule includes vaccines for diseases such as hepatitis B, rotavirus, diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib), inactivated poliovirus (IPV), influenza, measles, mumps, rubella (MMR), varicella (chickenpox), human papillomavirus (HPV), meningococcal, and pneumococcal diseases. The specific vaccines and the number of doses recommended can vary based on the individual’s age, health status, and other factors.
Vaccine Safety and Monitoring
The CDC, along with other health organizations, continuously monitors the safety of vaccines. Vaccine safety is a top priority, and the CDC uses several systems to track and analyze data on vaccine side effects and adverse events. These systems include the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS) and the Vaccine Safety Datalink (VSD). While vaccines, like any medication, can have side effects, the CDC emphasizes that the benefits of vaccination in preventing serious diseases far outweigh the risks of side effects.
Special Considerations for Immunization
There are special considerations for immunization in certain populations, including: - Pregnant women: Vaccines recommended during pregnancy include influenza and Tdap (tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis). - Travelers: Depending on the destination, additional vaccines may be recommended to protect against diseases prevalent in other parts of the world. - Healthcare workers: Healthcare professionals are recommended to receive certain vaccines to protect themselves and their patients from vaccine-preventable diseases. - Individuals with weakened immune systems: People with conditions such as HIV/AIDS or those undergoing chemotherapy may require special vaccination schedules.
Challenges and Misconceptions About Vaccines
Despite the proven benefits of vaccines, there are challenges and misconceptions that affect vaccination rates. Vaccine hesitancy, which is the reluctance or refusal to vaccinate despite the availability of vaccines, is a significant public health concern. Misconceptions about vaccine safety, efficacy, and necessity can lead to lower vaccination rates, increasing the risk of disease outbreaks. The CDC and other health organizations work to address these misconceptions through education and outreach.
📝 Note: It is essential to consult reputable sources, such as the CDC or the World Health Organization (WHO), for accurate information on vaccines and immunization guidelines.
Staying Up-to-Date with CDC Immunization Guidelines
The CDC regularly updates its immunization guidelines to reflect the latest scientific evidence and recommendations. Healthcare providers and the public can stay informed through various resources, including the CDC’s website, which provides detailed information on vaccine recommendations, schedules, and safety. Additionally, the CDC offers tools and resources for healthcare professionals to help them implement the recommended vaccination schedules and educate their patients about the importance of immunization.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, the CDC’s immunization guidelines are a cornerstone of public health, providing a framework for protecting individuals and communities against infectious diseases. As vaccine science continues to evolve, it is crucial that these guidelines are regularly updated to incorporate new evidence and vaccines. By following the CDC’s recommendations and staying informed, individuals can play a vital role in maintaining their health and contributing to the health of their communities.
What is the purpose of the CDC’s immunization guidelines?
+
The purpose of the CDC’s immunization guidelines is to provide recommendations on the use of vaccines to prevent infectious diseases in various populations, including children, adolescents, and adults.
How often are the CDC’s immunization guidelines updated?
+
The CDC updates its immunization guidelines regularly to reflect new scientific evidence, changes in disease epidemiology, and the licensure of new vaccines.
Where can I find the most current CDC immunization guidelines?
+
The most current CDC immunization guidelines can be found on the CDC’s official website, which provides detailed information on recommended vaccines, schedules, and safety.