5 Ways FOB Destination Works
Introduction to FOB Destination
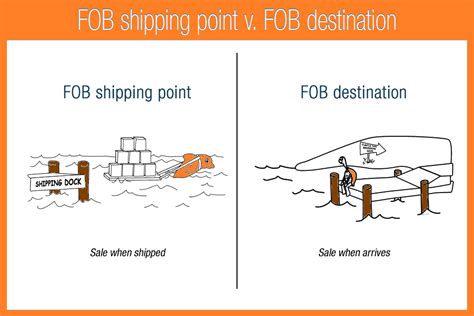
Free on Board (FOB) destination is a shipping term that indicates the seller is responsible for the goods until they reach the buyer’s destination. This term is often used in international trade, as it clearly defines the point at which the risk of loss or damage to the goods passes from the seller to the buyer. In this article, we will delve into the details of how FOB destination works and explore its implications for buyers and sellers.
How FOB Destination Works
When a seller agrees to deliver goods FOB destination, they are taking on a significant amount of responsibility. Here are the key aspects of how FOB destination works: * The seller is responsible for loading the goods onto the carrier’s vehicle. * The seller is responsible for paying the transportation costs to get the goods to the buyer’s destination. * The seller bears the risk of loss or damage to the goods until they reach the buyer’s destination. * The buyer’s responsibility begins once the goods have arrived at their destination.
Benefits of FOB Destination
FOB destination can be beneficial to both buyers and sellers. For buyers, it provides a high level of protection, as they do not have to worry about the goods being damaged or lost during transportation. For sellers, it can be a competitive advantage, as it demonstrates their commitment to customer satisfaction. Here are some of the benefits of FOB destination: * Reduced risk for buyers: With FOB destination, buyers do not have to worry about the goods being damaged or lost during transportation. * Increased customer satisfaction: By taking on the risk of transportation, sellers can increase customer satisfaction and build trust with their buyers. * Competitive advantage: Sellers who offer FOB destination may have a competitive advantage over those who do not.
5 Ways FOB Destination Works in Practice
Here are five ways that FOB destination works in practice: 1. FOB Destination and Insurance: When shipping FOB destination, sellers are responsible for insuring the goods against loss or damage. This means that if the goods are damaged or lost during transportation, the seller’s insurance will cover the cost of replacement or repair. 2. FOB Destination and Freight Costs: Sellers are responsible for paying the freight costs to get the goods to the buyer’s destination. This can include the cost of fuel, labor, and equipment. 3. FOB Destination and Customs Clearance: When shipping internationally, sellers may need to clear customs on behalf of the buyer. This can be a complex process, and sellers must ensure that they comply with all relevant regulations. 4. FOB Destination and Delivery: Sellers are responsible for delivering the goods to the buyer’s destination. This can include arranging for transportation, loading and unloading the goods, and ensuring that the goods are delivered on time. 5. FOB Destination and Returns: If the buyer needs to return the goods, the seller may be responsible for arranging and paying for the return transportation. This can be a complex process, and sellers must ensure that they have a clear returns policy in place.
Challenges of FOB Destination
While FOB destination can be beneficial to both buyers and sellers, there are also some challenges to consider. Here are some of the potential drawbacks: * Increased risk for sellers: By taking on the risk of transportation, sellers may be exposed to increased risk of loss or damage to the goods. * Higher costs for sellers: Sellers may need to pay higher costs for transportation, insurance, and customs clearance. * Complexity: FOB destination can be a complex process, especially when shipping internationally.
💡 Note: Sellers should carefully consider the terms of their FOB destination agreement to ensure that they understand their responsibilities and risks.
In summary, FOB destination is a shipping term that indicates the seller is responsible for the goods until they reach the buyer’s destination. While it can provide benefits to both buyers and sellers, there are also some challenges to consider. By understanding how FOB destination works and the implications for buyers and sellers, businesses can make informed decisions about their shipping arrangements.
As we reflect on the key points discussed, it’s clear that FOB destination is an important consideration for businesses involved in international trade. By taking on the risk of transportation, sellers can increase customer satisfaction and build trust with their buyers. However, sellers must also be aware of the potential drawbacks, including increased risk and higher costs. Ultimately, the decision to use FOB destination will depend on the specific needs and goals of the business.
What does FOB destination mean?
+
FOB destination means that the seller is responsible for the goods until they reach the buyer’s destination.
Who pays for transportation costs under FOB destination?
+
The seller pays for transportation costs under FOB destination.
What are the benefits of FOB destination for buyers?
+
The benefits of FOB destination for buyers include reduced risk of loss or damage to the goods during transportation.