Traveling Wave Ion Mobility Spectrometer
Introduction to Traveling Wave Ion Mobility Spectrometer
A Traveling Wave Ion Mobility Spectrometer (TWIMS) is a type of analytical instrument used to separate and identify ions based on their mobility in a gas phase. This technique has gained significant attention in recent years due to its ability to provide high-resolution separation of ions, making it an essential tool in various fields such as proteomics, metabolomics, and pharmaceutical research. In this article, we will delve into the principles of TWIMS, its components, and its applications.
Principles of Traveling Wave Ion Mobility Spectrometer
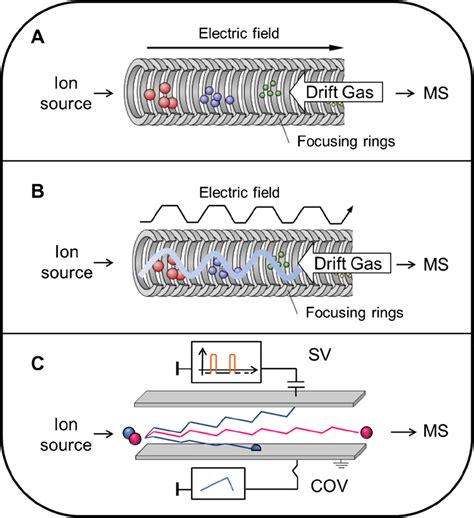
The TWIMS technique is based on the principle of ion mobility, which is the ability of ions to move through a gas phase under the influence of an electric field. In a TWIMS instrument, ions are generated using an ionization source, such as electrospray ionization (ESI) or nanoelectrospray ionization (nESI). The ions are then introduced into a drift tube, where they are separated based on their mobility. The drift tube is filled with a buffer gas, such as nitrogen or helium, which helps to reduce ion collisions and improve separation efficiency.
Components of Traveling Wave Ion Mobility Spectrometer
A typical TWIMS instrument consists of several key components, including: * Ions source: This is the component responsible for generating ions from the sample. Common ion sources used in TWIMS include ESI and nESI. * Drift tube: This is the component where ion separation takes place. The drift tube is filled with a buffer gas and is typically several meters long. * Traveling wave ion guide: This component is used to guide the ions through the drift tube and to separate them based on their mobility. * Mass analyzer: This component is used to detect the separated ions and to provide information about their mass-to-charge ratio.
How Traveling Wave Ion Mobility Spectrometer Works
The TWIMS technique works by applying a traveling wave to the ions as they move through the drift tube. The traveling wave is created by applying a series of voltage pulses to a series of electrodes that run along the length of the drift tube. The voltage pulses create an electric field that propels the ions through the drift tube, separating them based on their mobility. The separated ions are then detected using a mass analyzer, such as a time-of-flight (TOF) mass spectrometer.
Advantages of Traveling Wave Ion Mobility Spectrometer
TWIMS has several advantages over other ion mobility techniques, including: * High resolution: TWIMS can provide high-resolution separation of ions, making it possible to distinguish between ions with very similar mobilities. * High sensitivity: TWIMS can detect ions at very low concentrations, making it a useful tool for analyzing complex biological samples. * Fast analysis times: TWIMS can provide fast analysis times, making it possible to analyze large numbers of samples in a short amount of time.
Applications of Traveling Wave Ion Mobility Spectrometer
TWIMS has a wide range of applications in various fields, including: * Proteomics: TWIMS can be used to separate and identify proteins and peptides, making it a useful tool for proteomic research. * Metabolomics: TWIMS can be used to separate and identify metabolites, making it a useful tool for metabolomic research. * Pharmaceutical research: TWIMS can be used to analyze pharmaceutical compounds and to study their interactions with biological molecules.
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Proteomics | Separation and identification of proteins and peptides |
| Metabolomics | Separation and identification of metabolites |
| Pharmaceutical research | Analysis of pharmaceutical compounds and their interactions with biological molecules |
📝 Note: TWIMS is a powerful tool for separating and identifying ions, but it requires careful optimization of instrument parameters to achieve optimal performance.
As we have seen, TWIMS is a powerful analytical technique that has a wide range of applications in various fields. Its ability to provide high-resolution separation of ions makes it an essential tool for researchers who need to analyze complex biological samples. With its high sensitivity and fast analysis times, TWIMS is an ideal technique for large-scale biomolecular analysis.
In summary, TWIMS is a versatile and powerful analytical technique that has revolutionized the field of biomolecular analysis. Its ability to separate and identify ions with high resolution and sensitivity makes it an essential tool for researchers in various fields. As research continues to advance, we can expect to see even more innovative applications of TWIMS in the future.
What is Traveling Wave Ion Mobility Spectrometer?
+
Traveling Wave Ion Mobility Spectrometer (TWIMS) is a type of analytical instrument used to separate and identify ions based on their mobility in a gas phase.
What are the advantages of TWIMS?
+
TWIMS has several advantages, including high resolution, high sensitivity, and fast analysis times, making it a useful tool for analyzing complex biological samples.
What are the applications of TWIMS?
+
TWIMS has a wide range of applications in various fields, including proteomics, metabolomics, and pharmaceutical research, where it is used to separate and identify ions, such as proteins, peptides, and metabolites.