5 Vaccination Tips
Introduction to Vaccination
Vaccination is a crucial aspect of preventive healthcare, playing a significant role in protecting individuals and communities from infectious diseases. Vaccines work by stimulating the body’s immune system to recognize and fight pathogens, such as viruses or bacteria, without causing the disease itself. This not only prevents the vaccinated individual from getting sick but also helps in reducing the spread of diseases within a community, thereby protecting those who are more vulnerable, such as the elderly, young children, and people with certain health conditions. With the advancement in medical science, various types of vaccines have been developed, targeting a wide range of diseases. However, the effectiveness of vaccination largely depends on the individual’s understanding and adherence to vaccination guidelines.
Understanding Vaccination
Before delving into vaccination tips, it’s essential to have a basic understanding of how vaccines work and their importance. Immunization is the process whereby a person is made immune or resistant to an infectious disease, typically by the administration of a vaccine. Vaccines can be made from weakened or killed pathogens, their toxins, or one of their surface proteins. When a vaccine is administered, it stimulates the immune system to produce antibodies and immune cells that can recognize and attack the pathogen without causing the disease. This immunity can be categorized into two types: active immunity, which is achieved through vaccination or previous infection, and passive immunity, which is achieved through transfer of antibodies, such as from mother to child during breastfeeding.
Vaccination Tips
Given the importance of vaccination, here are five key tips to consider:
- Stay Informed: Keeping up-to-date with the latest recommendations on vaccinations is crucial. Different countries have their own vaccination schedules, and these can change based on new research and the emergence of new diseases. Staying informed helps in making sure you and your family are protected against preventable diseases.
- Follow the Schedule: Adhering to the vaccination schedule recommended by health authorities is vital. This schedule is designed to provide protection at the stages of life when it is most needed. Delaying vaccinations can leave individuals and communities vulnerable to outbreaks.
- Understand Vaccine Safety: Vaccines undergo rigorous testing for safety and efficacy before they are approved for public use. Despite common misconceptions, vaccines are safe and the risk of serious side effects is extremely low. Understanding the science behind vaccine safety can help in making informed decisions.
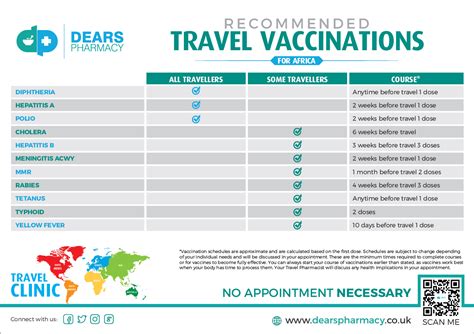
- Consider Travel Vaccinations: For individuals planning to travel, especially to areas with endemic diseases, certain vaccinations may be recommended or required. Researching the necessary vaccinations for travel destinations well in advance is important, as some vaccines require multiple doses over a period of time to be effective.
- Support Herd Immunity: Vaccination not only protects the individual but also contributes to herd immunity, which is crucial for protecting vulnerable members of the community who cannot receive vaccines due to medical reasons. By getting vaccinated, individuals play a role in preventing the spread of infectious diseases in their community.
Vaccination Benefits
The benefits of vaccination extend beyond individual health to contribute to public health and economic benefits. By reducing the incidence of infectious diseases, vaccinations: - Minimize the risk of outbreaks and epidemics. - Protect vulnerable populations, such as those with compromised immune systems. - Reduce the economic burden associated with healthcare costs and lost productivity due to illness. - Contribute to the global effort to eradicate diseases, as seen with the near eradication of polio and the elimination of smallpox.
💡 Note: Always consult with a healthcare professional before making any decisions regarding vaccination, especially if you have concerns or specific health conditions.
Vaccination Misconceptions
There are several misconceptions about vaccinations that can deter people from getting vaccinated. One of the most common is the belief that vaccines can cause the disease they are meant to prevent or that they contain harmful ingredients. However, these claims are not supported by scientific evidence. Vaccines are rigorously tested for safety and efficacy, and the ingredients used in vaccine production are strictly regulated and monitored. Another misconception is that if a person is healthy, they do not need vaccinations. However, even healthy individuals can contract and spread diseases, highlighting the importance of vaccination for community protection.
| Vaccine | Disease Prevented | Recommended Age |
|---|---|---|
| MMR | Measles, Mumps, Rubella | 12-15 months, 2nd dose at 4-6 years |
| DTaP | Diphtheria, Tetanus, Pertussis | 2, 4, 6 months, boosters at 15-18 months and 4-6 years |
| Polio | Polio | 2, 4, 6-18 months, booster at 4-6 years |
In summary, vaccination is a cornerstone of preventive healthcare, offering protection against a wide array of infectious diseases. By staying informed, following vaccination schedules, understanding vaccine safety, considering travel vaccinations, and supporting herd immunity, individuals can play a significant role in safeguarding their health and the health of their communities. The benefits of vaccination are multifaceted, ranging from individual protection to broader public health and economic advantages. As with any health decision, it’s essential to consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice on vaccinations.
What is the purpose of vaccination?
+
The primary purpose of vaccination is to stimulate the body’s immune system to recognize and fight pathogens, such as viruses or bacteria, without causing the disease itself, thereby providing immunity against infectious diseases.
How do vaccines work?
+
Vaccines work by introducing a weakened or killed pathogen, or a part of it, to the body, which then triggers the immune system to produce antibodies and immune cells that can recognize and attack the pathogen, providing immunity.
Are vaccines safe?
+
Vaccines undergo rigorous testing for safety and efficacy before they are approved for public use. The risk of serious side effects from vaccines is extremely low, making them a safe and effective way to prevent infectious diseases.