Strategic Trade Location AP World History
Introduction to Strategic Trade Locations
The concept of strategic trade locations has been a crucial aspect of international trade and commerce for centuries. In the context of AP World History, understanding the significance of these locations is essential to grasping the complexities of global interactions and exchanges. A strategic trade location refers to a place that offers a unique advantage in terms of commerce, such as access to multiple markets, control of vital trade routes, or possession of valuable resources. These locations have played a pivotal role in shaping the course of world history, influencing the rise and fall of empires, and facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures.
Key Characteristics of Strategic Trade Locations
Several factors contribute to a location’s strategic importance in trade. Some of the key characteristics include: * Geographical advantages: Locations with natural harbors, proximity to navigable rivers, or control of mountain passes can facilitate trade by providing easy access to multiple regions. * Access to resources: Areas rich in valuable commodities, such as silk, spices, or precious metals, can attract merchants and traders from afar. * Central position: Locations that serve as hubs or crossroads between different regions or trade routes can benefit from the flow of goods and ideas. * Political stability: Regions with stable governments or favorable trade policies can encourage investment and commerce.
Examples of Strategic Trade Locations in AP World History
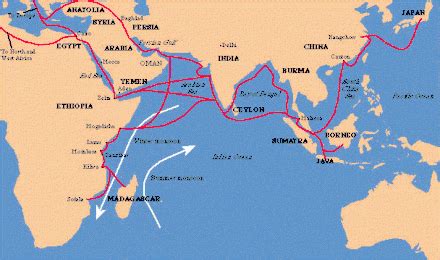
Throughout history, various locations have emerged as critical centers of trade, shaping the global economy and cultural exchange. Some notable examples include: * The Silk Road: This network of ancient trade routes connected China with the Mediterranean region, facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures between East Asia, the Middle East, and Europe. * The Indian Ocean trade network: This maritime trade system linked the Indian subcontinent with Southeast Asia, the Middle East, and East Africa, playing a vital role in the exchange of spices, textiles, and other valuable commodities. * The Strait of Malacca: This narrow waterway between the Malay Peninsula and the island of Sumatra controlled access to the Indian Ocean and the China Sea, making it a crucial location for trade between Asia and Europe. * The Mediterranean ports: Cities like Constantinople, Venice, and Genoa served as key hubs for trade between Europe, the Middle East, and North Africa, facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures.
The Impact of Strategic Trade Locations on Global Interactions
Strategic trade locations have had a profound impact on global interactions, influencing the course of world history in various ways. Some of the key effects include: * Cultural exchange: The exchange of goods and ideas between different regions has facilitated the spread of cultures, religions, and technologies. * Economic growth: Strategic trade locations have driven economic growth by creating new opportunities for trade, investment, and innovation. * Imperial expansion: The control of strategic trade locations has often been a key factor in the expansion of empires, as powerful states sought to dominate vital trade routes and resources. * Globalization: The increasing interconnectedness of the world economy has been driven in part by the development of strategic trade locations, which have facilitated the flow of goods, services, and ideas across borders.
| Location | Characteristics | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Silk Road | Network of ancient trade routes | Facilitated cultural exchange and economic growth between East Asia, the Middle East, and Europe |
| Indian Ocean trade network | Maritime trade system | Linked the Indian subcontinent with Southeast Asia, the Middle East, and East Africa, driving economic growth and cultural exchange |
| Strait of Malacca | Narrow waterway controlling access to the Indian Ocean and the China Sea | Crucial location for trade between Asia and Europe, influencing the rise and fall of empires |
💡 Note: The control of strategic trade locations has often been a key factor in the expansion of empires, as powerful states sought to dominate vital trade routes and resources.
In conclusion, strategic trade locations have played a vital role in shaping the course of world history, influencing the rise and fall of empires, and facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures. Understanding the characteristics and impact of these locations is essential to grasping the complexities of global interactions and exchanges. By examining the examples of the Silk Road, the Indian Ocean trade network, the Strait of Malacca, and the Mediterranean ports, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the significance of strategic trade locations in AP World History.
What is a strategic trade location?
+
A strategic trade location refers to a place that offers a unique advantage in terms of commerce, such as access to multiple markets, control of vital trade routes, or possession of valuable resources.
What are some key characteristics of strategic trade locations?
+
Some key characteristics include geographical advantages, access to resources, central position, and political stability.
How have strategic trade locations influenced global interactions?
+
Strategic trade locations have facilitated cultural exchange, driven economic growth, influenced imperial expansion, and contributed to globalization.