5 Ways Nutrients Travel
Introduction to Nutrient Transport
The human body is a complex system that relies on the efficient transport of nutrients to maintain proper functioning. Nutrients are essential for energy production, growth, and repair of tissues. There are several ways nutrients travel through the body, and understanding these mechanisms is crucial for appreciating the intricacies of human physiology. In this article, we will explore the different methods by which nutrients are transported, highlighting the key roles of the digestive system, circulatory system, and other bodily processes.
The Role of the Digestive System
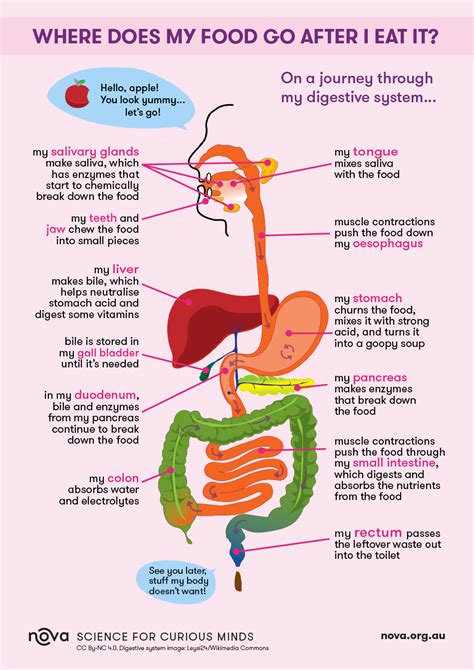
The digestive system plays a vital role in the breakdown and absorption of nutrients from the food we eat. The process begins in the mouth, where food is chewed and mixed with saliva that contains enzymes to break down carbohydrates. The food then passes through the esophagus into the stomach, where it is further broken down by stomach acids and enzymes. The partially digested food, now called chyme, then enters the small intestine, where most of our nutrient absorption takes place. The walls of the small intestine are lined with finger-like projections called villi, which increase the surface area for absorption. Nutrients are absorbed into the bloodstream through the villi and then transported to the liver for processing and distribution to the rest of the body.
Transport via the Circulatory System
The circulatory system, comprised of the heart, arteries, veins, and capillaries, is responsible for transporting nutrients from the digestive system to the rest of the body. Once nutrients are absorbed into the bloodstream, they are carried to the liver via the hepatic portal vein. The liver processes these nutrients, storing, modifying, or distributing them as necessary. The nutrients are then released into the general circulation, where they can be transported to tissues throughout the body. The circulatory system ensures that oxygen and nutrients are delivered to cells and that waste products are removed, maintaining the body’s homeostasis.
Different Methods of Nutrient Transport
There are several methods by which nutrients are transported within the body: - Simple Diffusion: This is the process by which substances move from an area of higher concentration to one of lower concentration. Oxygen and carbon dioxide are examples of substances that are transported through simple diffusion. - Facilitated Diffusion: This process involves the use of transport proteins to move substances across cell membranes. Glucose is transported into cells via facilitated diffusion. - Active Transport: This method requires energy (often in the form of ATP) to move substances against their concentration gradient. The absorption of amino acids and glucose in the intestine is an example of active transport. - Endocytosis: This is the process by which cells take in substances by engulfing them with their cell membrane. There are different types of endocytosis, including phagocytosis, pinocytosis, and receptor-mediated endocytosis. - Exocytosis: This is the process by which cells release substances to the outside by fusing vesicles containing these substances with the cell membrane.
Importance of Efficient Nutrient Transport
Efficient nutrient transport is crucial for maintaining the body’s overall health. Without proper nutrient delivery, cells cannot function correctly, leading to a range of health issues. For example, a deficiency in iron can lead to anemia, characterized by fatigue and weakness due to insufficient red blood cells or hemoglobin. Similarly, inadequate glucose transport can lead to conditions like diabetes, where the body either cannot produce enough insulin (Type 1 diabetes) or cannot effectively use the insulin it produces (Type 2 diabetes).
📝 Note: Understanding how nutrients travel through the body can help in managing and preventing diet-related disorders and diseases.
Factors Influencing Nutrient Transport
Several factors can influence how nutrients are transported within the body. These include: - Dietary Choices: The types of food we eat can significantly affect nutrient availability and absorption. A balanced diet that includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats is essential for optimal nutrient transport. - Health Status: Certain health conditions, such as celiac disease or Crohn’s disease, can impair nutrient absorption. Additionally, conditions that affect the circulatory system, like atherosclerosis, can hinder the transport of nutrients to tissues. - Lifestyle Factors: Lifestyle choices, including physical activity level and smoking status, can also impact nutrient transport and overall health.
| Nutrient | Primary Function | Transport Method |
|---|---|---|
| Oxygen | Energy Production | Simple Diffusion |
| Glucose | Energy Source | Facilitated Diffusion/Active Transport |
| Amino Acids | Protein Synthesis | Active Transport |
In summary, the transport of nutrients is a complex process that involves the coordinated effort of the digestive system, circulatory system, and various cellular processes. Understanding these mechanisms and the factors that influence them can provide valuable insights into maintaining optimal health and preventing nutrient-related disorders. By appreciating the intricacies of nutrient transport, individuals can make informed choices about their diet and lifestyle, contributing to overall well-being and resilience against disease. The efficient transport of nutrients is fundamental to the proper functioning of the body, highlighting the importance of a balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle in supporting this critical process.
What is the primary role of the digestive system in nutrient transport?
+
The primary role of the digestive system is to break down food into nutrients that can be absorbed and utilized by the body. This process involves both mechanical and chemical digestion, followed by absorption in the small intestine.
How does the circulatory system contribute to nutrient transport?
+
The circulatory system plays a crucial role in transporting nutrients from the digestive system to the rest of the body. It ensures that oxygen and nutrients are delivered to cells and that waste products are removed, maintaining the body’s homeostasis.
What factors can influence nutrient transport in the body?
+
Several factors can influence nutrient transport, including dietary choices, health status, and lifestyle factors. A balanced diet, overall health, and positive lifestyle choices are essential for optimal nutrient transport and utilization.